Page 301 - Veterinary diagnostic imaging birds exotic pets wildlife
P. 301
CHAPTER 26 III Rabbits 297
Extremital Fractures and Dislocations
Extremital fractures are usually the result of being
stepped on, caught in a door, or some other form of
momentary entrapment. Dislocations, with or without
associated fracture, occur most often to the digits,
usually as a result of catching a nail, for example, in
its enclosure (Figure 26-15).
Pelvic Fractures
Pelvic fractures are typically caused by crush injuries
such as a child falling or jumping on the pet rabbit.
Such fractures usually occur in groups and often
disrupt the weight-bearing ring, making it painful
to stand and impossible to hop (Figure 26-16).
These latter signs may be mistaken for a spinal cord
injury.
When radiographing the pelvis of a rabbit (or any
animal), the extended VD position is extremely painful
because of related fragment distraction. Much of the
pain associated with x-raying pelvic fractures can be
reduced by placing the animal on a medium-density
foam pad and by not fully extending the legs.
Osteoarthritis
Arthritis is caused either by excessive or abnormal
joint motion, for example, an untreated or unsuccess-
fully treated third-degree sprain of the genual joint
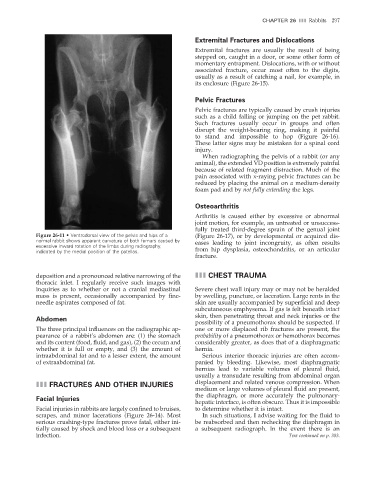
Figure 26-11 • Ventrodorsal view of the pelvis and hips of a (Figure 26-17), or by developmental or acquired dis-
normal rabbit shows apparent curvature of both femurs caused by eases leading to joint incongruity, as often results
excessive inward rotation of the limbs during radiography,
indicated by the medial position of the patellas. from hip dysplasia, osteochondritis, or an articular
fracture.
deposition and a pronounced relative narrowing of the III CHEST TRAUMA
thoracic inlet. I regularly receive such images with
inquiries as to whether or not a cranial mediastinal Severe chest wall injury may or may not be heralded
mass is present, occasionally accompanied by fi ne- by swelling, puncture, or laceration. Large rents in the
needle aspirates composed of fat. skin are usually accompanied by superficial and deep
subcutaneous emphysema. If gas is felt beneath intact
skin, then penetrating throat and neck injuries or the
Abdomen
possibility of a pneumothorax should be suspected. If
The three principal influences on the radiographic ap- one or more displaced rib fractures are present, the
pearance of a rabbit’s abdomen are: (1) the stomach probability of a pneumothorax or hemothorax becomes
and its content (food, fluid, and gas), (2) the cecum and considerably greater, as does that of a diaphragmatic
whether it is full or empty, and (3) the amount of hernia.
intraabdominal fat and to a lesser extent, the amount Serious interior thoracic injuries are often accom-
of extraabdominal fat. panied by bleeding. Likewise, most diaphragmatic
hernias lead to variable volumes of pleural fl uid,
usually a transudate resulting from abdominal organ
III FRACTURES AND OTHER INJURIES displacement and related venous compression. When
medium or large volumes of pleural fluid are present,
the diaphragm, or more accurately the pulmonary-
Facial Injuries
hepatic interface, is often obscure. Thus it is impossible
Facial injuries in rabbits are largely confined to bruises, to determine whether it is intact.
scrapes, and minor lacerations (Figure 26-14). Most In such situations, I advise waiting for the fl uid to
serious crushing-type fractures prove fatal, either ini- be reabsorbed and then rechecking the diaphragm in
tially caused by shock and blood loss or a subsequent a subsequent radiograph. In the event there is an
infection. Text continued on p. 303.
2/11/2008 11:12:49 AM
ch026-A02527.indd 297
ch026-A02527.indd 297 2/11/2008 11:12:49 AM