Page 94 - Veterinary diagnostic imaging birds exotic pets wildlife
P. 94
90 SECTION I III The Birds
fall, it still must find food and water and avoid preda-
Compound (Open) Fractures
tors. High-speed bullets are particularly dangerous;
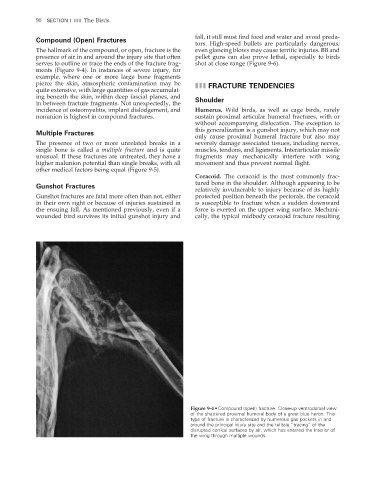
The hallmark of the compound, or open, fracture is the even glancing blows may cause terrific injuries. BB and
presence of air in and around the injury site that often pellet guns can also prove lethal, especially to birds
serves to outline or trace the ends of the fracture frag- shot at close range (Figure 9-6).
ments (Figure 9-4). In instances of severe injury, for
example, where one or more large bone fragments
pierce the skin, atmospheric contamination may be III FRACTURE TENDENCIES
quite extensive, with large quantities of gas accumulat-
ing beneath the skin, within deep fascial planes, and Shoulder
in between fracture fragments. Not unexpectedly, the
incidence of osteomyelitis, implant dislodgement, and Humerus. Wild birds, as well as cage birds, rarely
nonunion is highest in compound fractures. sustain proximal articular humeral fractures, with or
without accompanying dislocation. The exception to
this generalization is a gunshot injury, which may not
Multiple Fractures
only cause proximal humeral fracture but also may
The presence of two or more unrelated breaks in a severely damage associated tissues, including nerves,
single bone is called a multiple fracture and is quite muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Interarticular missile
unusual. If these fractures are untreated, they have a fragments may mechanically interfere with wing
higher malunion potential than single breaks, with all movement and thus prevent normal fl ight.
other medical factors being equal (Figure 9-5).
Coracoid. The coracoid is the most commonly frac-
tured bone in the shoulder. Although appearing to be
Gunshot Fractures
relatively invulnerable to injury because of its highly
Gunshot fractures are fatal more often than not, either protected position beneath the pectorals, the coracoid
in their own right or because of injuries sustained in is susceptible to fracture when a sudden downward
the ensuing fall. As mentioned previously, even if a force is exerted on the upper wing surface. Mechani-
wounded bird survives its initial gunshot injury and cally, the typical midbody coracoid fracture resulting
Figure 9-4 • Compound (open) fracture. Close-up ventrodorsal view
of the shattered proximal humeral body of a great blue heron. This
type of fracture is characterized by numerous gas pockets in and
around the principal injury site and the telltale “tracing” of the
disrupted cortical surfaces by air, which has entered the interior of
the wing through multiple wounds.
2/11/2008 10:55:23 AM
ch009-A02527.indd 90 2/11/2008 10:55:23 AM
ch009-A02527.indd 90