Page 34 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 34
CHAPTER 1 The Etiology of Cancer 13
1 Branch A: median survival 2.83 mo
6 6 0.8 Branch B: median survival 13.97 mo
p value 0.009
Chi-square 6.749
VetBooks.ir Greyhound (p) 4 2 4 2 Survival Probability 0.6
0.4
-log
153 aff (89M+64F)
0.2
114 unaff (65M+49F)
105,934 SNPs
0.9 0 0 Branch A Branch B 0
20
40
30
A 0 1 2 3 4 5 D 0 10 Time (months) 50 60
H
6 6
(p) 4 4
Rottweiler -log Cluster 1 Genes
80 aff (38M+42F) 2 2
55 unaff (27M+28F)
99,144 SNPs
1.05 0 0
B 0 1 2 3 4 5 E
4 4
(p) 3 3
Irish wolfhound -log 2 2 Cluster 2 Genes
28 aff (9M+19F)
62 unaff (27M+35F) 1 1
84,385 SNPs
0.96 0 0 1 23 45 67 89 10 12 14161820222426283032343638X
3
2
C 0 1 Expected -log p 4 5 F Chromosome
G -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
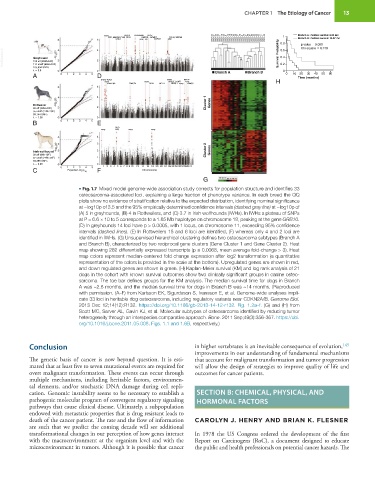
• Fig. 1.7 Mixed model genome-wide association study corrects for population structure and identifies 33
osteosarcoma-associated loci, explaining a large fraction of phenotype variance. In each breed the QQ
plots show no evidence of stratification relative to the expected distribution, identifying nominal significance
at −log10p of 3.5 and the 95% empirically determined confidence intervals (dashed gray line) at −log10p of
(A) 5 in greyhounds, (B) 4 in Rottweilers, and (C) 3.7 in Irish wolfhounds (IWHs). In IWHs a plateau of SNPs
at P = 6.6 × 10 to 5 corresponds to a 1.65 Mb haplotype on chromosome 18, peaking at the gene GRB10.
(D) In greyhounds 14 loci have p > 0.0005, with 1 locus, on chromosome 11, exceeding 95% confidence
intervals (dashed lines). (E) In Rottweilers 15 and 6 loci are identified, (F) whereas only 4 and 2 loci are
identified in IWHs. (G) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering defines two osteosarcoma subtypes (Branch A
and Branch B), characterized by two reciprocal gene clusters (Gene Cluster 1 and Gene Cluster 2). Heat
map showing 282 differentially expressed transcripts (p ≤ 0.0068, mean average fold-change > 3). Heat
map colors represent median-centered fold change expression after log2 transformation (a quantitative
representation of the colors is provided in the scale at the bottom). Upregulated genes are shown in red,
and down regulated genes are shown in green. (H) Kaplan-Meier survival (KM) and log rank analysis of 21
dogs in the cohort with known survival outcomes show two clinically significant groups in canine osteo-
sarcoma. The toe bar defines groups for the KM analysis. The median survival time for dogs in Branch
A was ∼2.8 months, and the median survival time for dogs in Branch B was ∼14 months. (Reproduced
with permission. (A–F) from Karlsson EK, Sigurdsson S, Ivansson E, et al. Genome-wide analyses impli-
cate 33 loci in heritable dog osteosarcoma, including regulatory variants near CDKN2A/B. Genome Biol.
2013 Dec 12;14(12):R132. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-12-r132. Fig. 1.2a–f. (G) and (H) from
Scott MC, Sarver AL, Gavin KJ, et al. Molecular subtypes of osteosarcoma identified by reducing tumor
heterogeneity through an interspecies comparative approach. Bone. 2011 Sep;49(3):356-367. https://doi.
org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.05.008. Figs. 1.1 and 1.6B, respectively.)
Conclusion in higher vertebrates is an inevitable consequence of evolution, 145
improvements in our understanding of fundamental mechanisms
The genetic basis of cancer is now beyond question. It is esti- that account for malignant transformation and tumor progression
mated that at least five to seven mutational events are required for will allow the design of strategies to improve quality of life and
overt malignant transformation. These events can occur through outcomes for cancer patients.
multiple mechanisms, including heritable factors, environmen-
tal elements, and/or stochastic DNA damage during cell repli-
cation. Genomic instability seems to be necessary to establish a SECTION B: CHEMICAL, PHYSICAL, AND
pathogenic molecular program of convergent regulatory signaling HORMONAL FACTORS
pathways that cause clinical disease. Ultimately, a subpopulation
endowed with metastatic properties that is drug resistant leads to
death of the cancer patient. The rate and the flow of information CAROLYN J. HENRY AND BRIAN K. FLESNER
are such that we predict the coming decade will see additional
transformational changes in our perception of how genes interact In 1978 the US Congress ordered the development of the first
with the macroenvironment at the organism level and with the Report on Carcinogens (RoC), a document designed to educate
microenvironment in tumors. Although it is possible that cancer the public and health professionals on potential cancer hazards. The