Page 1152 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1152
VetBooks.ir
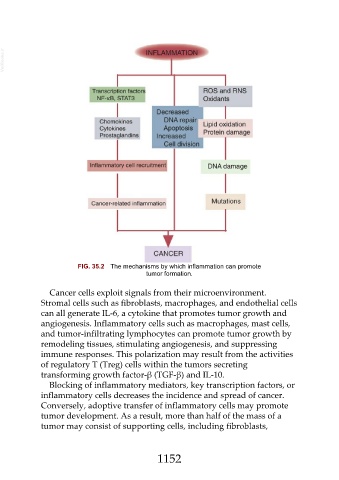
FIG. 35.2 The mechanisms by which inflammation can promote
tumor formation.
Cancer cells exploit signals from their microenvironment.
Stromal cells such as fibroblasts, macrophages, and endothelial cells
can all generate IL-6, a cytokine that promotes tumor growth and
angiogenesis. Inflammatory cells such as macrophages, mast cells,
and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes can promote tumor growth by
remodeling tissues, stimulating angiogenesis, and suppressing
immune responses. This polarization may result from the activities
of regulatory T (Treg) cells within the tumors secreting
transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-10.
Blocking of inflammatory mediators, key transcription factors, or
inflammatory cells decreases the incidence and spread of cancer.
Conversely, adoptive transfer of inflammatory cells may promote
tumor development. As a result, more than half of the mass of a
tumor may consist of supporting cells, including fibroblasts,
1152