Page 348 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 348
VetBooks.ir
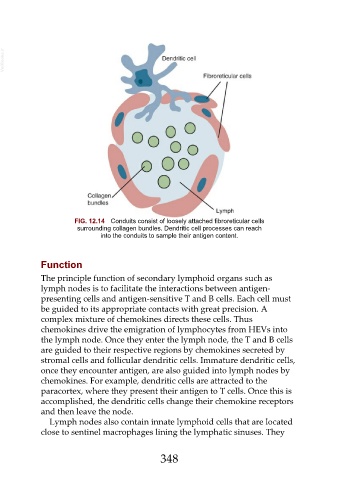
FIG. 12.14 Conduits consist of loosely attached fibroreticular cells
surrounding collagen bundles. Dendritic cell processes can reach
into the conduits to sample their antigen content.
Function
The principle function of secondary lymphoid organs such as
lymph nodes is to facilitate the interactions between antigen-
presenting cells and antigen-sensitive T and B cells. Each cell must
be guided to its appropriate contacts with great precision. A
complex mixture of chemokines directs these cells. Thus
chemokines drive the emigration of lymphocytes from HEVs into
the lymph node. Once they enter the lymph node, the T and B cells
are guided to their respective regions by chemokines secreted by
stromal cells and follicular dendritic cells. Immature dendritic cells,
once they encounter antigen, are also guided into lymph nodes by
chemokines. For example, dendritic cells are attracted to the
paracortex, where they present their antigen to T cells. Once this is
accomplished, the dendritic cells change their chemokine receptors
and then leave the node.
Lymph nodes also contain innate lymphoid cells that are located
close to sentinel macrophages lining the lymphatic sinuses. They
348