Page 771 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 771
VetBooks.ir Types of Immunization Procedures
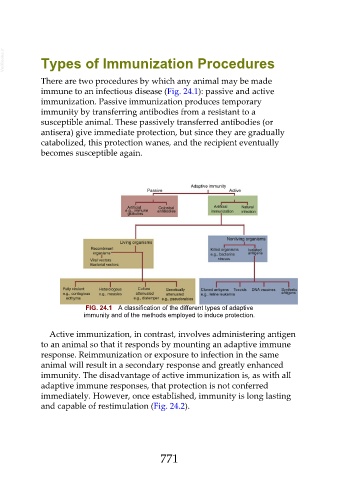
There are two procedures by which any animal may be made
immune to an infectious disease (Fig. 24.1): passive and active
immunization. Passive immunization produces temporary
immunity by transferring antibodies from a resistant to a
susceptible animal. These passively transferred antibodies (or
antisera) give immediate protection, but since they are gradually
catabolized, this protection wanes, and the recipient eventually
becomes susceptible again.
FIG. 24.1 A classification of the different types of adaptive
immunity and of the methods employed to induce protection.
Active immunization, in contrast, involves administering antigen
to an animal so that it responds by mounting an adaptive immune
response. Reimmunization or exposure to infection in the same
animal will result in a secondary response and greatly enhanced
immunity. The disadvantage of active immunization is, as with all
adaptive immune responses, that protection is not conferred
immediately. However, once established, immunity is long lasting
and capable of restimulation (Fig. 24.2).
771