Page 177 - Problem-Based Feline Medicine
P. 177
10 – THE CAT WITH TACHYCARDIA, BRADYCARDIA OR AN IRREGULAR RHYTHM 169
LEADII at 50 mm/sec 1 cm/m//v
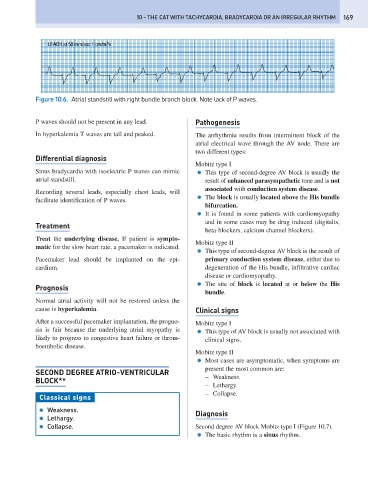
Figure 10.6. Atrial standstill with right bundle branch block. Note lack of P waves.
P waves should not be present in any lead. Pathogenesis
In hyperkalemia T waves are tall and peaked. The arrhythmia results from intermittent block of the
atrial electrical wave through the AV node. There are
two different types:
Differential diagnosis
Mobitz type I
Sinus bradycardia with isoelectric P waves can mimic ● This type of second-degree AV block is usually the
atrial standstill. result of enhanced parasympathetic tone and is not
associated with conduction system disease.
Recording several leads, especially chest leads, will
● The block is usually located above the His bundle
facilitate identification of P waves.
bifurcation.
● It is found in some patients with cardiomyopathy
and in some cases may be drug induced (digitalis,
Treatment
beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers).
Treat the underlying disease. If patient is sympto-
Mobitz type II
matic for the slow heart rate, a pacemaker is indicated.
● This type of second-degree AV block is the result of
Pacemaker lead should be implanted on the epi- primary conduction system disease, either due to
cardium. degeneration of the His bundle, infiltrative cardiac
disease or cardiomyopathy.
● The site of block is located at or below the His
Prognosis
bundle.
Normal atrial activity will not be restored unless the
cause is hyperkalemia. Clinical signs
After a successful pacemaker implantation, the progno- Mobitz type I
sis is fair because the underlying atrial myopathy is ● This type of AV block is usually not associated with
likely to progress to congestive heart failure or throm- clinical signs.
boembolic disease.
Mobitz type II
● Most cases are asymptomatic, when symptoms are
present the most common are:
SECOND DEGREE ATRIO-VENTRICULAR
– Weakness.
BLOCK**
– Lethargy.
– Collapse.
Classical signs
● Weakness.
Diagnosis
● Lethargy.
● Collapse. Second degree AV block Mobitz type I (Figure 10.7).
● The basic rhythm is a sinus rhythm.