Page 179 - Problem-Based Feline Medicine
P. 179
10 – THE CAT WITH TACHYCARDIA, BRADYCARDIA OR AN IRREGULAR RHYTHM 171
Pathogenesis The QRS complex morphology is more commonly
abnormal and is wide and bizarre.
This arrhythmia results from complete block of the
atrial electrical wave through the AV node.
Differential diagnosis
The site of block is at or below the bundle of His.
Advanced second-degree AV block may mimic inter-
The most common etiologies are:
mittent third-degree AV block.
● Cardiomyopathy.
● Degeneration, fibrosis or infiltration of the conduc-
tion system.
Treatment
Clinical signs Many cats are asymptomatic with this arrhythmia;
therefore treatment is not indicated for these patients.
In some cases, no clinical signs are present.
If symptoms of collapse or weakness are present med-
If there are clinical signs these are due to a combination
ical therapy can be tried:
of the underlying disease and the degree of bradycardia.
● Theophylline 20 mg/kg PO every 24 h.
Usually the heart rate is below 100 beats per minute ● Propantheline bromide 7.5 mg/cat PO every 8–12 h.
and the signs are: ● Terbutaline 0.625 mg/cat PO every 8–12 h.
● Weakness.
Responses to medical therapy are variable and usually
● Lethargy.
temporary and a pacemaker is indicated.
● Collapse.
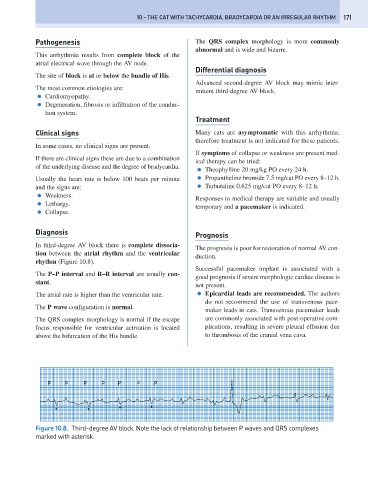
Diagnosis Prognosis
In third-degree AV block there is complete dissocia-
The prognosis is poor for restoration of normal AV con-
tion between the atrial rhythm and the ventricular
duction.
rhythm (Figure 10.8).
Successful pacemaker implant is associated with a
The P–P interval and R–R interval are usually con-
good prognosis if severe morphologic cardiac disease is
stant.
not present.
The atrial rate is higher than the ventricular rate. ● Epicardial leads are recommended. The authors
do not recommend the use of transvenous pace-
The P wave configuration is normal.
maker leads in cats. Transvenous pacemaker leads
The QRS complex morphology is normal if the escape are commonly associated with post-operative com-
focus responsible for ventricular activation is located plications, resulting in severe pleural effusion due
above the bifurcation of the His bundle. to thrombosis of the cranial vena cava.
P P P P P P P
* * * *
Figure 10.8. Third-degree AV block. Note the lack of relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
marked with asterisk.