Page 254 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 254
236 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
Na ion pump in lateral plasma membrane), drawing water pancreatis). The endocrine component of the pancreas is
+
VetBooks.ir from the cells. The nuclei lie in the basal third of the cell. In described in Chapter 9, ‘Endocrine system’. The exocrine
addition to absorptive epithelial cells, the lining of the gall portion consists of a:
bladder contains isolated secretory mucous cells (goblet
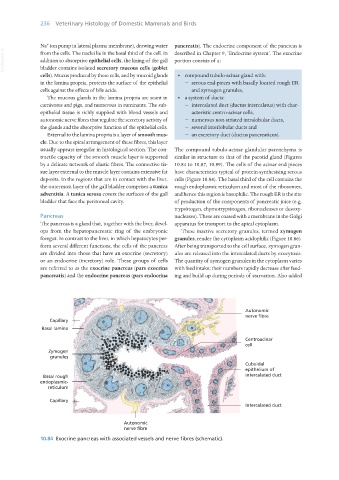
cells). Mucus produced by these cells, and by mucoid glands • compound tubulo-acinar gland with:
in the lamina propria, protects the surface of the epithelial − serous end-pieces with basally located rough ER
cells against the effects of bile acids. and zymogen granules,
The mucous glands in the lamina propria are scant in • a system of ducts:
carnivores and pigs, and numerous in ruminants. The sub- − intercalated duct (ductus intercalatus) with char-
epithelial tissue is richly supplied with blood vessels and acteristic centro-acinar cells,
autonomic nerve fibres that regulate the secretory activity of − numerous non-striated intralobular ducts,
the glands and the absorptive function of the epithelial cells. − several interlobular ducts and
External to the lamina propria is a layer of smooth mus- − an excretory duct (ductus pancreaticus).
cle. Due to the spiral arrangement of these fibres, this layer
usually appears irregular in histological section. The con- The compound tubulo-acinar glandular parenchyma is
tractile capacity of the smooth muscle layer is supported similar in structure to that of the parotid gland (Figures
by a delicate network of elastic fibres. The connective tis- 10.84 to 10.87, 10.89). The cells of the acinar end pieces
sue layer external to the muscle layer contains extensive fat have characteristics typical of protein-synthesising serous
deposits. In the regions that are in contact with the liver, cells (Figure 10.84). The basal third of the cell contains the
the outermost layer of the gall bladder comprises a tunica rough endoplasmic reticulum and most of the ribosomes,
adventitia. A tunica serosa covers the surfaces of the gall and hence this region is basophilic. The rough ER is the site
bladder that face the peritoneal cavity. of production of the components of pancreatic juice (e.g.
trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, ribonucleases or desoxy-
Pancreas nucleases). These are coated with a membrane in the Golgi
The pancreas is a gland that, together with the liver, devel- apparatus for transport to the apical cytoplasm.
ops from the hepatopancreatic ring of the embryonic These inactive secretory granules, termed zymogen
foregut. In contrast to the liver, in which hepatocytes per- granules, render the cytoplasm acidophilic (Figure 10.86).
form several different functions, the cells of the pancreas After being transported to the cell surface, zymogen gran-
are divided into those that have an exocrine (secretory) ules are released into the intercalated ducts by exocytosis.
or an endocrine (incretory) role. These groups of cells The quantity of zymogen granules in the cytoplasm varies
are referred to as the exocrine pancreas (pars exocrina with feed intake; their numbers rapidly decrease after feed-
pancreatis) and the endocrine pancreas (pars endocrina ing and build up during periods of starvation. Also added
10.84 Exocrine pancreas with associated vessels and nerve fibres (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 236 16/07/2019 15:02