Page 259 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 259
Respiratory system (apparatus respiratorius) 241
VetBooks.ir
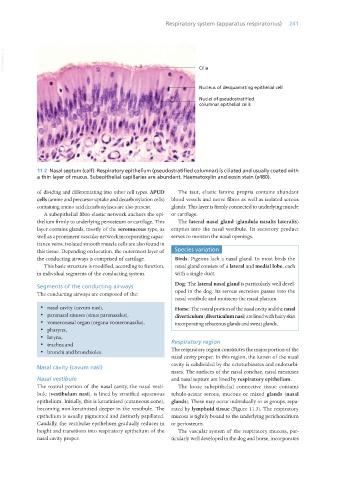
11.2 Nasal septum (calf). Respiratory epithelium (pseudostratified columnar) is ciliated and usually coated with
a thin layer of mucus. Subepithelial capillaries are abundant. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x480).
of dividing and differentiating into other cell types. APUD The taut, elastic lamina propria contains abundant
cells (amine and precursor uptake and decarboxylation cells) blood vessels and nerve fibres as well as isolated serous
containing amino acid decarboxylases are also present. glands. This layer is firmly connected to underlying muscle
A subepithelial fibro-elastic network anchors the epi- or cartilage.
thelium firmly to underlying periosteum or cartilage. This The lateral nasal gland (glandula nasalis lateralis)
layer contains glands, mostly of the seromucous type, as empties into the nasal vestibule. Its secretory product
well as a prominent vascular network incorporating capac- serves to moisten the nasal openings.
itance veins. Isolated smooth muscle cells are also found in
this tissue. Depending on location, the outermost layer of Species variation
the conducting airways is comprised of cartilage. Birds: Pigeons lack a nasal gland. In most birds the
This basic structure is modified, according to function, nasal gland consists of a lateral and medial lobe, each
in individual segments of the conducting system. with a single duct.
Segments of the conducting airways Dog: The lateral nasal gland is particularly well devel-
The conducting airways are composed of the: oped in the dog. Its serous secretion passes into the
nasal vestibule and moistens the nasal planum.
· nasal cavity (cavum nasi), Horse: The rostral portion of the nasal cavity and the nasal
· paranasal sinuses (sinus paranasales), diverticulum (diverticulum nasi) are lined with hairy skin
· vomeronasal organ (organa vomeronasalia), incorporating sebaceous glands and sweat glands.
· pharynx,
· larynx,
· trachea and Respiratory region
· bronchi and bronchioles. The respiratory region constitutes the major portion of the
nasal cavity proper. In this region, the lumen of the nasal
Nasal cavity (cavum nasi) cavity is subdivided by the ectoturbinates and endoturbi-
nates. The surfaces of the nasal conchae, nasal meatuses
Nasal vestibule and nasal septum are lined by respiratory epithelium.
The rostral portion of the nasal cavity, the nasal vesti- The loose subepithelial connective tissue contains
bule (vestibulum nasi), is lined by stratified squamous tubulo-acinar serous, mucous or mixed glands (nasal
epithelium. Initially, this is keratinised (cutaneous zone), glands). These may occur individually or as groups, sepa-
becoming non-keratinised deeper in the vestibule. The rated by lymphoid tissue (Figure 11.3). The respiratory
epithelium is usually pigmented and distinctly papillated. mucosa is tightly bound to the underlying perichondrium
Caudally, the vestibular epithelium gradually reduces in or periosteum.
height and transitions into respiratory epithelium of the The vascular system of the respiratory mucosa, par-
nasal cavity proper. ticularly well developed in the dog and horse, incorporates
Vet Histology.indb 241 16/07/2019 15:02