Page 60 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 60
42 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
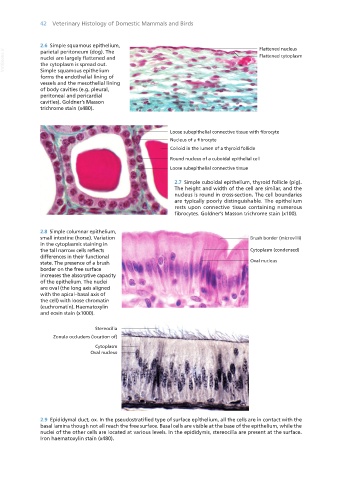
2.6 Simple squamous epithelium,
VetBooks.ir nuclei are largely flattened and
parietal peritoneum (dog). The
the cytoplasm is spread out.
Simple squamous epithelium
forms the endothelial lining of
vessels and the mesothelial lining
of body cavities (e.g. pleural,
peritoneal and pericardial
cavities). Goldner’s Masson
trichrome stain (x480).
2.7 Simple cuboidal epithelium, thyroid follicle (pig).
The height and width of the cell are similar, and the
nucleus is round in cross-section. The cell boundaries
are typically poorly distinguishable. The epithelium
rests upon connective tissue containing numerous
fibrocytes. Goldner’s Masson trichrome stain (x100).
2.8 Simple columnar epithelium,
small intestine (horse). Variation Brush border (microvilli)
in the cytoplasmic staining in
the tall narrow cells reflects Cytoplasm (condensed)
differences in their functional
state. The presence of a brush Oval nucleus
border on the free surface
increases the absorptive capacity
of the epithelium. The nuclei
are oval (the long axis aligned
with the apical–basal axis of
the cell) with loose chromatin
(euchromatin). Haematoxylin
and eosin stain (x1000).
Stereocilia
Zonula occludens (location of)
Cytoplasm
Oval nucleus
2.9 Epididymal duct, ox. In the pseudostratified type of surface epithelium, all the cells are in contact with the
basal lamina though not all reach the free surface. Basal cells are visible at the base of the epithelium, while the
nuclei of the other cells are located at various levels. In the epididymis, stereocilia are present at the surface.
Iron haematoxylin stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 42 16/07/2019 14:54