Page 61 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 61
Epithelial tissue (textus epithelialis) 43
VetBooks.ir
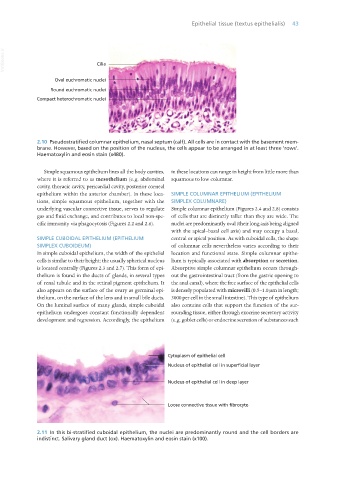
2.10 Pseudostratified columnar epithelium, nasal septum (calf). All cells are in contact with the basement mem-
brane. However, based on the position of the nucleus, the cells appear to be arranged in at least three ‘rows’.
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x480).
Simple squamous epithelium lines all the body cavities, in these locations can range in height from little more than
where it is referred to as mesothelium (e.g. abdominal squamous to low columnar.
cavity, thoracic cavity, pericardial cavity, posterior corneal
epithelium within the anterior chamber). In these loca- SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM (EPITHELIUM
tions, simple squamous epithelium, together with the SIMPLEX COLUMNARE)
underlying vascular connective tissue, serves to regulate Simple columnar epithelium (Figures 2.4 and 2.8) consists
gas and fluid exchange, and contributes to local non-spe- of cells that are distinctly taller than they are wide. The
cific immunity via phagocytosis (Figures 2.2 and 2.6). nuclei are predominantly oval (their long axis being aligned
with the apical–basal cell axis) and may occupy a basal,
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM (EPITHELIUM central or apical position. As with cuboidal cells, the shape
SIMPLEX CUBOIDEUM) of columnar cells nevertheless varies according to their
In simple cuboidal epithelium, the width of the epithelial location and functional state. Simple columnar epithe-
cells is similar to their height; the usually spherical nucleus lium is typically associated with absorption or secretion.
is located centrally (Figures 2.3 and 2.7). This form of epi- Absorptive simple columnar epithelium occurs through-
thelium is found in the ducts of glands, in several types out the gastrointestinal tract (from the gastric opening to
of renal tubule and in the retinal pigment epithelium. It the anal canal), where the free surface of the epithelial cells
also appears on the surface of the ovary as germinal epi- is densely populated with microvilli (0.5–1.0 μm in length;
thelium, on the surface of the lens and in small bile ducts. 3000 per cell in the small intestine). This type of epithelium
On the luminal surface of many glands, simple cuboidal also contains cells that support the function of the sur-
epithelium undergoes constant functionally dependent rounding tissue, either through exocrine secretory activity
development and regression. Accordingly, the epithelium (e.g. goblet cells) or endocrine secretion of substances such
2.11 In this bi-stratified cuboidal epithelium, the nuclei are predominantly round and the cell borders are
indistinct. Salivary gland duct (ox). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x100).
Vet Histology.indb 43 16/07/2019 14:54