Page 85 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 85
Connective and supportive tissues (textus connectivus) 67
Collagen fibres stain with eosin (red), aniline blue (blue) tissue. Type IV is found in basal laminae. Type V collagen
VetBooks.ir and with the dye light green (from Masson’s trichrome; is also associated with the basal lamina, and is distributed
green). They can also be identified using polarised light throughout connective tissue stroma. Types IV and V
microscopy based on their banding pattern. Biochemically, collagen are rich in hydroxyproline.
collagen fibres are divided into many different types, of
which at least five are currently considered of morphologi- RETICULAR FIBRES (FIBRA RETICULARIS)
cal significance. Their distinguishing features include the Reticular fibres derive their name from their finely
amino acid sequence of the pro-α-chain and the number branched, mesh-like arrangement (Figure 3–8). They form
of saccharide residues. flexible three-dimensional networks within various organs
Type I collagen is the most abundant form of body and tissues (liver, kidney, glands, vessels), are associated
collagen (90%), occurring in tendons, fascia, bones, ves- with basal laminae and form a meshwork around ten-
sels, internal organs and dentin. It consists of two identical dons, ligaments and muscle fibres. Reticular fibres play an
chains (α ) and an additional, different, chain (α ). important supportive role in lympho- and haemoreticular
1 2
Types II and III consist of three α -chains that vary tissues (spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow) by providing
1
in their amino acid composition (e.g. in hydroxyproline, a flexible scaffold.
hydroxylysyl or cysteine residues). Type II collagen forms Immunohistochemical techniques reveal that reticular
the structural collagen of hyaline cartilage. Type III col- fibres are composed of type III collagen. Precursor forms
lagen occurs in the walls of vessels, in internal organs (e.g. are produced within fibroblasts, with polymerisation and
liver, kidney, spleen), in skin and in embryonic connective formation of microfibrils occurring in the extracellular
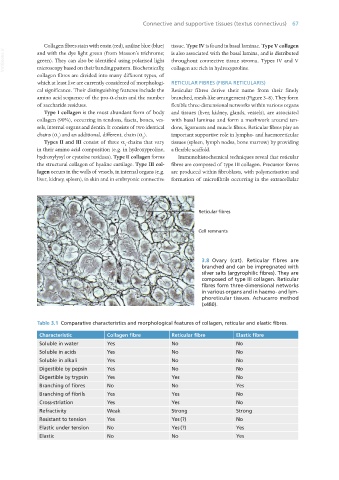
3.8 Ovary (cat). Reticular fibres are
branched and can be impregnated with
silver salts (argyrophilic fibres). They are
composed of type III collagen. Reticular
fibres form three-dimensional networks
in various organs and in haemo- and lym-
phoreticular tissues. Achucarro method
(x480).
Table 3.1 Comparative characteristics and morphological features of collagen, reticular and elastic fibres.
Characteristic Collagen fibre Reticular fibre Elastic fibre
Soluble in water Yes No No
Soluble in acids Yes No No
Soluble in alkali Yes No No
Digestible by pepsin Yes No No
Digestible by trypsin Yes Yes No
Branching of fibres No No Yes
Branching of fibrils Yes Yes No
Cross-striation Yes Yes No
Refractivity Weak Strong Strong
Resistant to tension Yes Yes (?) No
Elastic under tension No Yes (?) Yes
Elastic No No Yes
Vet Histology.indb 67 16/07/2019 14:55