Page 87 - Manual of Equine Field Surgery
P. 87
Distal Check Ligament Desmotomy 83
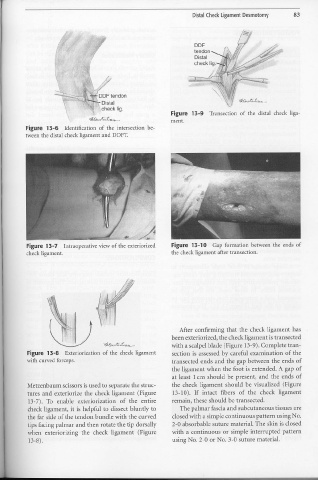
DDF
tendon
Distal
check lig.
, \ DDF tendon
, Distal
\' · ·\ check Jig.
'! Figure 13-9 Transection of the distal check liga-
~t;.;f,(.t.,/l,-- ment.
Figure 13-6 Identification of the intersection be-
tween the distal check ligament and DDFT.
..
!!!l:~~~allllili~.:.:::m==:::::=-~_:! ~:.__. ;lo.
Figure 13-7 Intraoperative view of the exteriorized Figure 13-10 Gap formation between the ends of
check ligament. the check ligament after transection.
After confirming that the check ligament has
been exteriorized, the check ligament is transected
'4£.~t; . .t;w,,._. with a scalpel blade (Figure 13-9). Complete tran-
Figure 13-8 Exteriorization of the check ligament section is assessed by careful examination of the
with curved forceps. transected ends and the gap between the ends of
the ligament when the foot is extended. A gap of
at least 1 cm should be present, and the ends of
Metzenbaum scissors is used to separate the struc- the check ligament should be visualized (Figure
tures and exteriorize the check ligament (Figure 13-10). If intact fibers of the check ligament
13- 7). To enable exteriorization of the entire remain, these should be transected.
check ligament, it is helpful to dissect bluntly to The palmar fascia and subcutaneous tissues are
the far side of the tendon bundle with the curved closed with a simple continuous pattern using No.
tips facing palmar and then rotate the tip dorsally 2-0 absorbable suture material. The skin is closed
when exteriorizing the check ligament (Figure with a continuous or simple interrupted pattern
13-8). using No. 2-0 or No. 3-0 suture material.
- --- -~-- ~ - ----- -
- ,.- --- - -