Page 80 - Natural Antioxidants, Applications in Foods of Animal Origin
P. 80
Natural Antioxidants: Occurrence and Their Role in Food Preservation 59
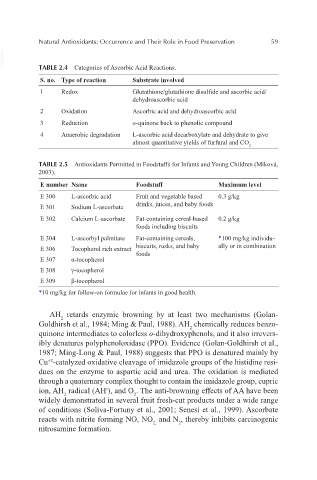
VetBooks.ir TABLE 2.4 Categories of Ascorbic Acid Reactions.
S. no. Type of reaction Substrate involved
1 Redox Glutathione/glutathione disulfide and ascorbic acid/
dehydroascorbic acid
2 Oxidation Ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid
3 Reduction o-quinone back to phenolic compound
4 Anaerobic degradation L-ascorbic acid decarboxylate and dehydrate to give
almost quantitative yields of furfural and CO
2
TABLE 2.5 Antioxidants Permitted in Foodstuffs for Infants and Young Children (Miková,
2003).
E number Name Foodstuff Maximum level
E 300 L-ascorbic acid Fruit and vegetable based 0.3 g/kg
E 301 Sodium L-ascorbate drinks, juices, and baby foods
E 302 Calcium L-ascorbate Fat-containing cereal-based 0.2 g/kg
foods including biscuits
E 304 L-ascorbyl palmitate Fat-containing cereals, *100 mg/kg individu-
E 306 Tocopherol rich extract biscuits, rusks, and baby ally or in combination
foods
E 307 α-tocopherol
E 308 γ-tocopherol
E 309 β-tocopherol
*10 mg/kg for follow-on formulae for infants in good health.
AH retards enzymic browning by at least two mechanisms (Golan-
2
Goldhirsh et al., 1984; Ming & Paul, 1988). AH chemically reduces benzo-
2
quinone intermediates to colorless o-dihydroxyphenols, and it also irrevers-
ibly denatures polyphenoloxidase (PPO). Evidence (Golan-Goldhirsh et al.,
1987; Ming-Long & Paul, 1988) suggests that PPO is denatured mainly by
Cu -catalyzed oxidative cleavage of imidazole groups of the histidine resi-
+2
dues on the enzyme to aspartic acid and urea. The oxidation is mediated
through a quaternary complex thought to contain the imidazole group, cupric
ion, AH radical (AH ), and O . The anti-browning effects of AA have been
•
2
2
widely demonstrated in several fruit fresh-cut products under a wide range
of conditions (Soliva-Fortuny et al., 2001; Senesi et al., 1999). Ascorbate
reacts with nitrite forming NO, NO and N , thereby inhibits carcinogenic
2
2,
nitrosamine formation.