Page 1222 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1222
1160 Section 10 Renal and Genitourinary Disease
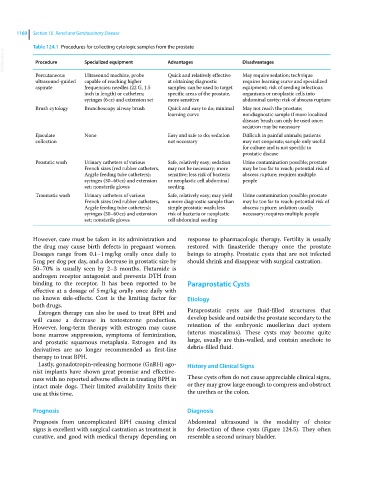
Table 124.1 Procedures for collecting cytologic samples from the prostate
VetBooks.ir Procedure Specialized equipment Advantages Disadvantages
Percutaneous Ultrasound machine, probe Quick and relatively effective May require sedation; technique
ultrasound‐guided capable of reaching higher at obtaining diagnostic requires learning curve and specialized
aspirate frequencies; needles (22 G, 1.5 samples; can be used to target equipment; risk of seeding infectious
inch in length) or catheters; specific areas of the prostate, organisms or neoplastic cells into
syringes (6 cc) and extension set more sensitive abdominal cavity; risk of abscess rupture
Brush cytology Bronchoscopy airway brush Quick and easy to do; minimal May not reach the prostate;
learning curve nondiagnostic sample if more localized
disease; brush can only be used once;
sedation may be necessary
Ejaculate None Easy and safe to do; sedation Difficult in painful animals; patients
collection not necessary may not cooperate; sample only useful
for culture and is not specific to
prostatic disease
Prostatic wash Urinary catheters of various Safe, relatively easy; sedation Urine contamination possible; prostate
French sizes (red rubber catheters, may not be necessary; more may be too far to reach; potential risk of
Argyle feeding tube catheters); sensitive; less risk of bacteria abscess rupture; requires multiple
syringes (30–60 cc) and extension or neoplastic cell abdominal people
set; nonsterile gloves seeding
Traumatic wash Urinary catheters of various Safe, relatively easy; may yield Urine contamination possible; prostate
French sizes (red rubber catheters, a more diagnostic sample than may be too far to reach; potential risk of
Argyle feeding tube catheters); simple prostatic wash; less abscess rupture; sedation usually
syringes (30–60 cc) and extension risk of bacteria or neoplastic necessary; requires multiple people
set; nonsterile gloves cell abdominal seeding
However, care must be taken in its administration and response to pharmacologic therapy. Fertility is usually
the drug may cause birth defects in pregnant women. restored with finasteride therapy once the prostate
Dosages range from 0.1–1 mg/kg orally once daily to beings to atrophy. Prostatic cysts that are not infected
5 mg per dog per day, and a decrease in prostatic size by should shrink and disappear with surgical castration.
50–70% is usually seen by 2–3 months. Flutamide is
androgen receptor antagonist and prevents DTH from
binding to the receptor. It has been reported to be Paraprostatic Cysts
effective at a dosage of 5 mg/kg orally once daily with
no known side‐effects. Cost is the limiting factor for Etiology
both drugs.
Estrogen therapy can also be used to treat BPH and Paraprostatic cysts are fluid‐filled structures that
will cause a decrease in testosterone production. develop beside and outside the prostate secondary to the
However, long‐term therapy with estrogen may cause retention of the embryonic muellerian duct system
bone marrow suppression, symptoms of feminization, (uterus masculinus). These cysts may become quite
and prostatic squamous metaplasia. Estrogen and its large, usually are thin‐walled, and contain anechoic to
derivatives are no longer recommended as first‐line debris‐filled fluid.
therapy to treat BPH.
Lastly, gonadotropin‐releasing hormone (GnRH) ago- History and Clinical Signs
nist implants have shown great promise and effective-
ness with no reported adverse effects in treating BPH in These cysts often do not cause appreciable clinical signs,
intact male dogs. Their limited availability limits their or they may grow large enough to compress and obstruct
use at this time. the urethra or the colon.
Prognosis Diagnosis
Prognosis from uncomplicated BPH causing clinical Abdominal ultrasound is the modality of choice
signs is excellent with surgical castration as treatment is for detection of these cysts (Figure 124.5). They often
curative, and good with medical therapy depending on resemble a second urinary bladder.