Page 1577 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1577
171 Skeletal Development and Homeostasis 1515
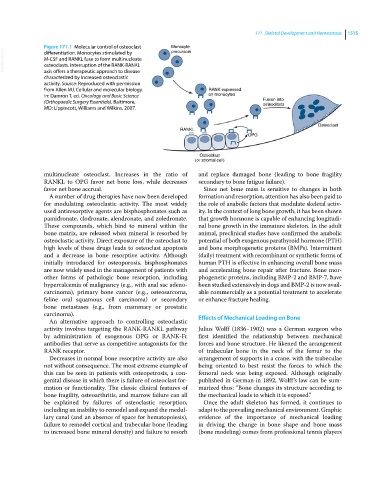
Figure 171.1 Molecular control of osteoclast Monocyte
VetBooks.ir M‐CSF and RANKL fuse to form multinucleate
precursors
differentiation. Monocytes stimulated by
osteoclasts. Interruption of the RANK‐RANKL
axis offers a therapeutic approach to disease
characterized by increased osteoclastic
activity. Source: Reproduced with permission
from Allen MJ. Cellular and molecular biology. RANK expressed
In: Damron T, ed. Oncology and Basic Science on monocytes
(Orthopaedic Surgery Essentials). Baltimore, Fusion into
osteoclasts
MD: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2007.
Osteoclast
RANKL
OPG
Osteoblast
(or stromal cell)
multinucleate osteoclast. Increases in the ratio of and replace damaged bone (leading to bone fragility
RANKL to OPG favor net bone loss, while decreases secondary to bone fatigue failure).
favor net bone accrual. Since net bone mass is sensitive to changes in both
A number of drug therapies have now been developed formation and resorption, attention has also been paid to
for modulating osteoclastic activity. The most widely the role of anabolic factors that modulate skeletal activ-
used antiresorptive agents are bisphosphonates such as ity. In the context of long bone growth, it has been shown
pamidronate, clodronate, alendronate, and zoledronate. that growth hormone is capable of enhancing longitudi-
These compounds, which bind to mineral within the nal bone growth in the immature skeleton. In the adult
bone matrix, are released when mineral is resorbed by animal, preclinical studies have confirmed the anabolic
osteoclastic activity. Direct exposure of the osteoclast to potential of both exogenous parathyroid hormone (PTH)
high levels of these drugs leads to osteoclast apoptosis and bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Intermittent
and a decrease in bone resorptive activity. Although (daily) treatment with recombinant or synthetic forms of
initially introduced for osteoporosis, bisphosphonates human PTH is effective in enhancing overall bone mass
are now widely used in the management of patients with and accelerating bone repair after fracture. Bone mor-
other forms of pathologic bone resorption, including phogenetic proteins, including BMP‐2 and BMP‐7, have
hypercalcemia of malignancy (e.g., with anal sac adeno- been studied extensively in dogs and BMP‐2 is now avail-
carcinoma), primary bone cancer (e.g., osteosarcoma, able commercially as a potential treatment to accelerate
feline oral squamous cell carcinoma) or secondary or enhance fracture healing.
bone metastases (e.g., from mammary or prostatic
carcinoma). Effects of Mechanical Loading on Bone
An alternative approach to controlling osteoclastic
activity involves targeting the RANK‐RANKL pathway Julius Wolff (1836–1902) was a German surgeon who
by administration of exogenous OPG or RANK‐Fc first identified the relationship between mechanical
antibodies that serve as competitive antagonists for the forces and bone structure. He likened the arrangement
RANK receptor. of trabecular bone in the neck of the femur to the
Decreases in normal bone resorptive activity are also arrangement of supports in a crane, with the trabeculae
not without consequence. The most extreme example of being oriented to best resist the forces to which the
this can be seen in patients with osteopetrosis, a con- femoral neck was being exposed. Although originally
genital disease in which there is failure of osteoclast for- published in German in 1892, Wolff’s law can be sum-
mation or functionality. The classic clinical features of marized thus: “Bone changes its structure according to
bone fragility, osteoarthritis, and marrow failure can all the mechanical loads to which it is exposed.”
be explained by failures of osteoclastic resorption, Once the adult skeleton has formed, it continues to
including an inability to remodel and expand the medul- adapt to the prevailing mechanical environment. Graphic
lary canal (and an absence of space for hematopoiesis), evidence of the importance of mechanical loading
failure to remodel cortical and trabecular bone (leading in driving the change in bone shape and bone mass
to increased bone mineral density) and failure to resorb (bone modeling) comes from professional tennis players