Page 345 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 345
VetBooks.ir mature. They are ovoid clusters of cells divided into a light and
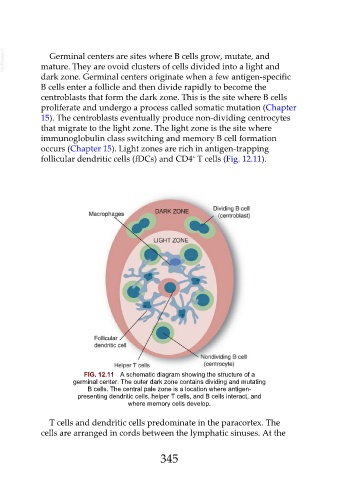
Germinal centers are sites where B cells grow, mutate, and
dark zone. Germinal centers originate when a few antigen-specific
B cells enter a follicle and then divide rapidly to become the
centroblasts that form the dark zone. This is the site where B cells
proliferate and undergo a process called somatic mutation (Chapter
15). The centroblasts eventually produce non-dividing centrocytes
that migrate to the light zone. The light zone is the site where
immunoglobulin class switching and memory B cell formation
occurs (Chapter 15). Light zones are rich in antigen-trapping
+
follicular dendritic cells (fDCs) and CD4 T cells (Fig. 12.11).
FIG. 12.11 A schematic diagram showing the structure of a
germinal center. The outer dark zone contains dividing and mutating
B cells. The central pale zone is a location where antigen-
presenting dendritic cells, helper T cells, and B cells interact, and
where memory cells develop.
T cells and dendritic cells predominate in the paracortex. The
cells are arranged in cords between the lymphatic sinuses. At the
345