Page 609 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 609
VetBooks.ir
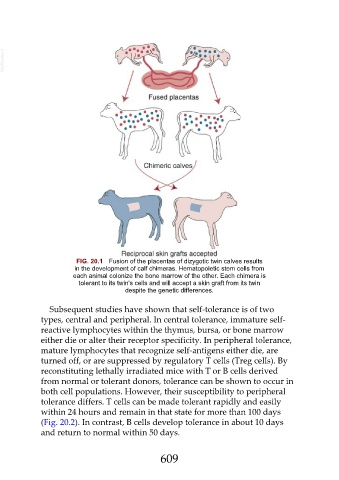
FIG. 20.1 Fusion of the placentas of dizygotic twin calves results
in the development of calf chimeras. Hematopoietic stem cells from
each animal colonize the bone marrow of the other. Each chimera is
tolerant to its twin's cells and will accept a skin graft from its twin
despite the genetic differences.
Subsequent studies have shown that self-tolerance is of two
types, central and peripheral. In central tolerance, immature self-
reactive lymphocytes within the thymus, bursa, or bone marrow
either die or alter their receptor specificity. In peripheral tolerance,
mature lymphocytes that recognize self-antigens either die, are
turned off, or are suppressed by regulatory T cells (Treg cells). By
reconstituting lethally irradiated mice with T or B cells derived
from normal or tolerant donors, tolerance can be shown to occur in
both cell populations. However, their susceptibility to peripheral
tolerance differs. T cells can be made tolerant rapidly and easily
within 24 hours and remain in that state for more than 100 days
(Fig. 20.2). In contrast, B cells develop tolerance in about 10 days
and return to normal within 50 days.
609