Page 618 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 618
VetBooks.ir
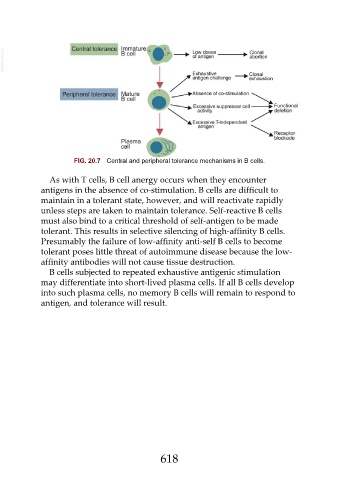
FIG. 20.7 Central and peripheral tolerance mechanisms in B cells.
As with T cells, B cell anergy occurs when they encounter
antigens in the absence of co-stimulation. B cells are difficult to
maintain in a tolerant state, however, and will reactivate rapidly
unless steps are taken to maintain tolerance. Self-reactive B cells
must also bind to a critical threshold of self-antigen to be made
tolerant. This results in selective silencing of high-affinity B cells.
Presumably the failure of low-affinity anti-self B cells to become
tolerant poses little threat of autoimmune disease because the low-
affinity antibodies will not cause tissue destruction.
B cells subjected to repeated exhaustive antigenic stimulation
may differentiate into short-lived plasma cells. If all B cells develop
into such plasma cells, no memory B cells will remain to respond to
antigen, and tolerance will result.
618