Page 635 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 635
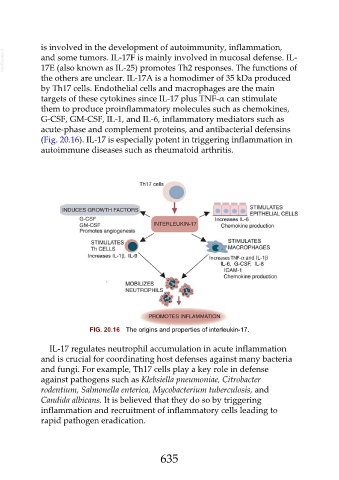
is involved in the development of autoimmunity, inflammation,
VetBooks.ir and some tumors. IL-17F is mainly involved in mucosal defense. IL-
17E (also known as IL-25) promotes Th2 responses. The functions of
the others are unclear. IL-17A is a homodimer of 35 kDa produced
by Th17 cells. Endothelial cells and macrophages are the main
targets of these cytokines since IL-17 plus TNF-α can stimulate
them to produce proinflammatory molecules such as chemokines,
G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-1, and IL-6, inflammatory mediators such as
acute-phase and complement proteins, and antibacterial defensins
(Fig. 20.16). IL-17 is especially potent in triggering inflammation in
autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
FIG. 20.16 The origins and properties of interleukin-17.
IL-17 regulates neutrophil accumulation in acute inflammation
and is crucial for coordinating host defenses against many bacteria
and fungi. For example, Th17 cells play a key role in defense
against pathogens such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter
rodentium, Salmonella enterica, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and
Candida albicans. It is believed that they do so by triggering
inflammation and recruitment of inflammatory cells leading to
rapid pathogen eradication.
635