Page 168 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 168
150 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
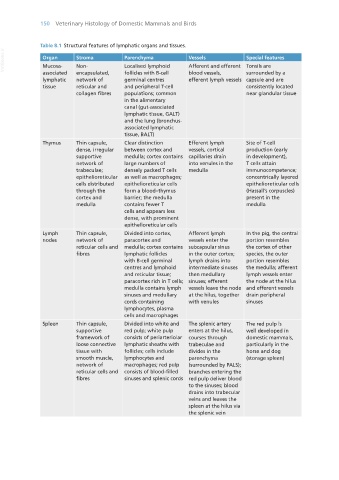
Table 8.1 Structural features of lymphatic organs and tissues.
VetBooks.ir Organ Stroma Parenchyma Vessels Special features
Localised lymphoid
Non-
Mucosa-
Afferent and efferent Tonsils are
associated encapsulated, follicles with B-cell blood vessels, surrounded by a
lymphatic network of germinal centres efferent lymph vessels capsule and are
tissue reticular and and peripheral T-cell consistently located
collagen fibres populations; common near glandular tissue
in the alimentary
canal (gut-associated
lymphatic tissue, GALT)
and the lung (bronchus-
associated lymphatic
tissue, BALT)
Thymus Thin capsule, Clear distinction Efferent lymph Site of T-cell
dense, irregular between cortex and vessels, cortical production (early
supportive medulla; cortex contains capillaries drain in development),
network of large numbers of into venules in the T cells attain
trabeculae; densely packed T cells medulla immunocompetence;
epithelioreticular as well as macrophages; concentrically layered
cells distributed epithelioreticular cells epithelioreticular cells
through the form a blood–thymus (Hassall’s corpuscles)
cortex and barrier; the medulla present in the
medulla contains fewer T medulla
cells and appears less
dense, with prominent
epithelioreticular cells
Lymph Thin capsule, Divided into cortex, Afferent lymph In the pig, the central
nodes network of paracortex and vessels enter the portion resembles
reticular cells and medulla; cortex contains subcapsular sinus the cortex of other
fibres lymphatic follicles in the outer cortex; species, the outer
with B-cell germinal lymph drains into portion resembles
centres and lymphoid intermediate sinuses the medulla; afferent
and reticular tissue; then medullary lymph vessels enter
paracortex rich in T cells; sinuses; efferent the node at the hilus
medulla contains lymph vessels leave the node and efferent vessels
sinuses and medullary at the hilus, together drain peripheral
cords containing with venules sinuses
lymphocytes, plasma
cells and macrophages
Spleen Thin capsule, Divided into white and The splenic artery The red pulp is
supportive red pulp; white pulp enters at the hilus, well developed in
framework of consists of periarteriolar courses through domestic mammals,
loose connective lymphatic sheaths with trabeculae and particularly in the
tissue with follicles; cells include divides in the horse and dog
smooth muscle, lymphocytes and parenchyma (storage spleen)
network of macrophages; red pulp (surrounded by PALS);
reticular cells and consists of blood-filled branches entering the
fibres sinuses and splenic cords red pulp deliver blood
to the sinuses; blood
drains into trabecular
veins and leaves the
spleen at the hilus via
the splenic vein
Vet Histology.indb 150 16/07/2019 14:59