Page 209 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 209
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 191
The duct system begins at the secretory end piece with Parotid salivary gland
VetBooks.ir the intralobular ducts. These are composed of the inter- The parotid gland is a compound acinar gland. In most
calated duct, into which the secretory unit empties, and domestic mammals it is a serous gland, though isolated
the striated duct, so named because of basal striations in mucous secretory units may occur peripherally in carnivores.
the columnar epithelium (Figures 10.13 to 10.15 and 10.17). The principal organelles within the acidophilic, granular cyto-
Outside the small glandular lobules, intralobular ducts plasm of the secretory cells (see Figure 2.46) are mitochondria
are continued by interlobular ducts (Figures 10.13 and and organelles associated with protein synthesis (ribosomes
10.16), interlobar and main ducts. Smooth muscle cells are and polyribosomes, rough ER). Apically, the area of the
found outside the larger ducts. The stratified epithelium secretory cell surface is increased by numerous microvilli.
of main ducts contains occasional goblet cells. The size of The low cuboidal epithelium of the intercalated
the lumen gradually increases from the intercalated duct ducts becomes columnar in the striated duct. The basal
to the main duct (Figure 10.13). striations from which the ducts derive their name are
visible with the light microscope. They are formed by
regular infoldings of the plasmalemma enclosing stacks of
mitochondria. The presence of an enlarged surface area
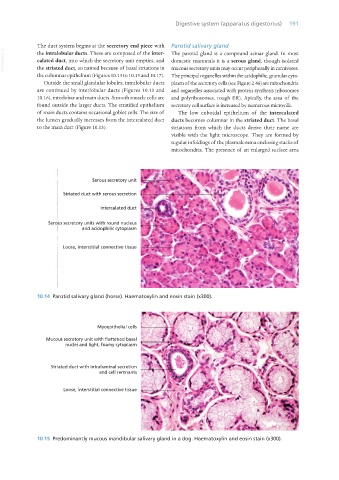
10.14 Parotid salivary gland (horse). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x300).
Myoepithelial cells
Mucous secretory unit with flattened basal
nuclei and light, foamy cytoplasm
Striated duct with intraluminal secretion
and cell remnants
Loose, interstitial connective tissue
10.15 Predominantly mucous mandibular salivary gland in a dog. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x300).
Vet Histology.indb 191 16/07/2019 15:00