Page 206 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 206
188 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
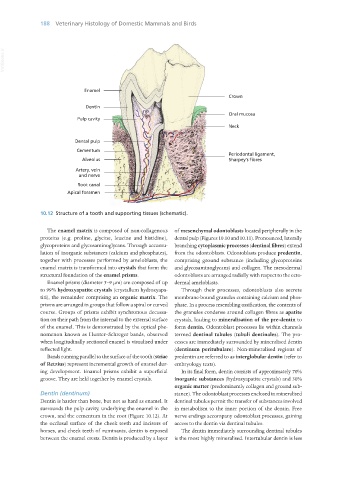
10.12 Structure of a tooth and supporting tissues (schematic).
The enamel matrix is composed of non-collagenous of mesenchymal odontoblasts located peripherally in the
proteins (e.g. proline, glycine, leucine and histidine), dental pulp (Figures 10.10 and 10.11). Pronounced, laterally
glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans. Through accumu- branching cytoplasmic processes (dentinal fibres) extend
lation of inorganic substances (calcium and phosphates), from the odontoblasts. Odontoblasts produce predentin,
together with processes performed by ameloblasts, the comprising ground substance (including glycoproteins
enamel matrix is transformed into crystals that form the and glycosaminoglycans) and collagen. The mesodermal
structural foundation of the enamel prisms. odontoblasts are arranged radially with respect to the ecto-
Enamel prisms (diameter 5–9 μm) are composed of up dermal ameloblasts.
to 99% hydroxyapatite crystals (crystallum hydroxyapa- Through their processes, odontoblasts also secrete
titi), the remainder comprising an organic matrix. The membrane-bound granules containing calcium and phos-
prisms are arranged in groups that follow a spiral or curved phate. In a process resembling ossification, the contents of
course. Groups of prisms exhibit synchronous decussa- the granules condense around collagen fibres as apatite
tion on their path from the internal to the external surface crystals, leading to mineralisation of the pre-dentin to
of the enamel. This is demonstrated by the optical phe- form dentin. Odontoblast processes lie within channels
nomenon known as Hunter–Schreger bands, observed termed dentinal tubules (tubuli dentinales). The pro-
when longitudinally sectioned enamel is visualised under cesses are immediately surrounded by mineralised dentin
reflected light. (dentinum peritubulare). Non-mineralised regions of
Bands running parallel to the surface of the tooth (striae predentin are referred to as interglobular dentin (refer to
of Retzius) represent incremental growth of enamel dur- embryology texts).
ing development. Enamel prisms exhibit a superficial In its final form, dentin consists of approximately 70%
groove. They are held together by enamel crystals. inorganic substances (hydroxyapatite crystals) and 30%
organic matter (predominantly collagen and ground sub-
Dentin (dentinum) stance). The odontoblast processes enclosed in mineralised
Dentin is harder than bone, but not as hard as enamel. It dentinal tubules permit the transfer of substances involved
surrounds the pulp cavity, underlying the enamel in the in metabolism to the inner portion of the dentin. Free
crown, and the cementum in the root (Figure 10.12). At nerve endings accompany odontoblast processes, gaining
the occlusal surface of the cheek teeth and incisors of access to the dentin via dentinal tubules.
horses, and cheek teeth of ruminants, dentin is exposed The dentin immediately surrounding dentinal tubules
between the enamel crests. Dentin is produced by a layer is the most highly mineralised. Intertubular dentin is less
Vet Histology.indb 188 16/07/2019 15:00