Page 301 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 301
Male reproductive system (organa genitalia masculina) 283
VetBooks.ir
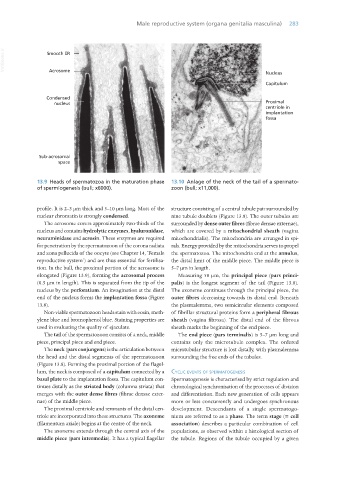
13.9 Heads of spermatozoa in the maturation phase 13.10 Anlage of the neck of the tail of a spermato-
of spermiogenesis (bull; x6000). zoon (bull; x11,000).
profile. It is 2–3 μm thick and 5–10 μm long. Most of the structure consisting of a central tubule pair surrounded by
nuclear chromatin is strongly condensed. nine tubule doublets (Figure 13.8). The outer tubules are
The acrosome covers approximately two-thirds of the surrounded by dense outer fibres (fibrae densae externae),
nucleus and contains hydrolytic enzymes, hyaluronidase, which are covered by a mitochondrial sheath (vagina
neuraminidase and acrosin. These enzymes are required mitochondrialis). The mitochondria are arranged in spi-
for penetration by the spermatozoon of the corona radiata rals. Energy provided by the mitochondria serves to propel
and zona pellucida of the oocyte (see Chapter 14, ‘Female the spermatozoa. The mitochondria end at the annulus,
reproductive system’) and are thus essential for fertilisa- the distal limit of the middle piece. The middle piece is
tion. In the bull, the proximal portion of the acrosome is 5–7 μm in length.
elongated (Figure 13.9), forming the acrosomal process Measuring 50 μm, the principal piece (pars princi-
(0.5 μm in length). This is separated from the tip of the palis) is the longest segment of the tail (Figure 13.8).
nucleus by the perforatium. An invagination at the distal The axoneme continues through the principal piece, the
end of the nucleus forms the implantation fossa (Figure outer fibres decreasing towards its distal end. Beneath
13.8). the plasmalemma, two semicircular elements composed
Non-viable spermatozoon heads stain with eosin, meth- of fibrillar structural proteins form a peripheral fibrous
ylene blue and bromophenol blue. Staining properties are sheath (vagina fibrosa). The distal end of the fibrous
used in evaluating the quality of ejaculate. sheath marks the beginning of the end piece.
The tail of the spermatozoon consists of a neck, middle The end piece (pars terminalis) is 5–7 μm long and
piece, principal piece and end piece. contains only the microtubule complex. The ordered
The neck (pars conjungens) is the articulation between microtubular structure is lost distally, with plasmalemma
the head and the distal segments of the spermatozoon surrounding the free ends of the tubules.
(Figure 13.8). Forming the proximal portion of the flagel-
lum, the neck is composed of a capitulum connected by a cyclic events of sPeRmatogenesis
basal plate to the implantation fossa. The capitulum con- Spermatogenesis is characterised by strict regulation and
tinues distally as the striated body (columna striata) that chronological synchronisation of the processes of division
merges with the outer dense fibres (fibrae densae exter- and differentiation. Each new generation of cells appears
nae) of the middle piece. more or less concurrently and undergoes synchronous
The proximal centriole and remnants of the distal cen- development. Descendants of a single spermatogo-
triole are incorporated into these structures. The axoneme nium are referred to as a phase. The term stage (= cell
(filamentum axiale) begins at the centre of the neck. association) describes a particular combination of cell
The axoneme extends through the central axis of the populations, as observed within a histological section of
middle piece (pars intermedia). It has a typical flagellar the tubule. Regions of the tubule occupied by a given
Vet Histology.indb 283 16/07/2019 15:04