Page 160 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 160
144 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
behind. Position the index finger and thumb on either
side of the head just below the eyes. Very gently hold the Blind spot
bird with the rest of the fingers in a “cage” like hold
rather than touching the bird. This will help prevent the
possibility of suffocating the bird. Once out of the cage,
resting the bird on a folded towel will help make them
comfortable and you can grasp their feet at that time. If
you can cover their head that will calm them as well.
Others suggest allowing the bird to step off a perch and Field of vision Field of vision
onto your hand or arm. Bring the bird close to your
chest with its breast facing yours. Reach up from behind
with the other hand and grasp the bird around the head
in the same manner as described previously. Again, cage
your fingers around the thorax. If the bird is small, like a
parakeet or cockatiel, you can pin their feet with your
little finger. If the bird is larger, like an amazon or cock-
atoo, you will need to use the other hand to control the
feet. Once they are caught you can extend a wing for Blind spot
flight feather or toenail trims.
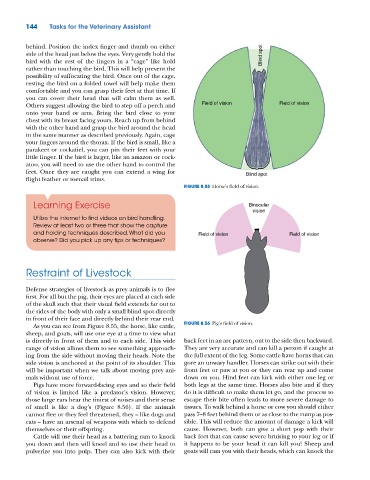
FIGURE 8.55 Horse’s field of vision.
Learning Exercise Binocular
vision
Utilize the internet to find videos on bird handling.
Review at least two or three that show the capture
and holding techniques described. What did you Field of vision Field of vision
observe? Did you pick up any tips or techniques?
Restraint of Livestock
Defense strategies of livestock as prey animals is to flee
first. For all but the pig, their eyes are placed at each side
of the skull such that their visual field extends far out to
the sides of the body with only a small blind spot directly
in front of their face and directly behind their rear end.
As you can see from Figure 8.55, the horse, like cattle, FIGURE 8.56 Pig’s field of vision.
sheep, and goats, will use one eye at a time to view what
is directly in front of them and to each side. This wide back feet in an arc pattern, out to the side then backward.
range of vision allows them to see something approach- They are very accurate and can kill a person if caught at
ing from the side without moving their heads. Note the the full extent of the leg. Some cattle have horns that can
side vision is anchored at the point of its shoulder. This gore an unwary handler. Horses can strike out with their
will be important when we talk about moving prey ani- front feet or paw at you or they can rear up and come
mals without use of force. down on you. Hind feet can kick with either one leg or
Pigs have more forward‐facing eyes and so their field both legs at the same time. Horses also bite and if they
of vision is limited like a predator’s vision. However, do it is difficult to make them let go, and the process to
those large ears hear the tiniest of noises and their sense escape their bite often leads to more severe damage to
of smell is like a dog’s (Figure 8.56). If the animals tissues. To walk behind a horse or cow you should either
cannot flee or they feel threatened, they – like dogs and pass 7–8 feet behind them or as close to the rump as pos-
cats – have an arsenal of weapons with which to defend sible. This will reduce the amount of damage a kick will
themselves or their offspring. cause. However, both can give a short pop with their
Cattle will use their head as a battering ram to knock back feet that can cause severe bruising to your leg or if
you down and then will kneel and to use their head to it happens to be your head it can kill you! Sheep and
pulverize you into pulp. They can also kick with their goats will ram you with their heads, which can knock the