Page 40 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 40
Approach to Evaluating Arrhythmias
– Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) AV block: PR VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
Ventricular arrhythmias are abnormal spontaneous
interval gradually prolongs until conduction
VetBooks.ir across the AV node fails, hence no QRS depolarizations that originate in any location in the
ventricle. The occurrence of three or more ventricular
complex occurs following the P (dropped
beat). premature contractions (VPCs) in a row is termed
– Mobitz type II AV block: The PR interval is VT. Descriptions of ventricular arrhythmias often
usually constant before a dropped beat occurs. include whether or not the morphology of all VPCs is
This is considered a more advanced form of similar (monomorphic) or different (polymorphic),
block that occurs lower in the His bundle and occurs as a single VPC, two VPCs in a row (couplet),
may thus progress to complete heart block. or three or more VPCs in a row (VT). Furthermore,
• In third-degree (complete) AV block (Fig. 3.12), a period of VT is often described as persisting
none of the P waves conduct through the AV less than 30 seconds (nonsustained) or more than
node, thus the atrial and ventricular activities 30 seconds (sustained). Breed-specific ventricular
are completely independent (AV dissociation). arrhythmias occur especially in Boxers, Doberman
The atrial rate is faster than the ventricular Pinschers, and German Shepherd dogs. An analysis
rate. The escape rhythm is either junctional or algorithm for differentiation of wide QRS complex
ventricular in origin. arrhythmias is shown in Figure 3.3 p. 22.
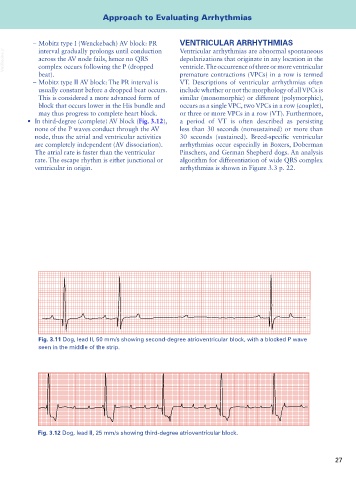
Fig. 3.11 Dog, lead II, 50 mm/s showing second-degree atrioventricular block, with a blocked P wave
seen in the middle of the strip.
Fig. 3.12 Dog, lead II, 25 mm/s showing third-degree atrioventricular block.
27