Page 382 - The Veterinary Care of the Horse
P. 382
Causes
Bacteria may enter a joint:
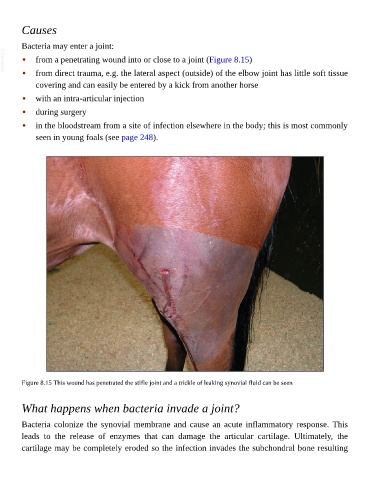
VetBooks.ir • from a penetrating wound into or close to a joint (Figure 8.15)
• from direct trauma, e.g. the lateral aspect (outside) of the elbow joint has little soft tissue
covering and can easily be entered by a kick from another horse
• with an intra-articular injection
• during surgery
• in the bloodstream from a site of infection elsewhere in the body; this is most commonly
seen in young foals (see page 248).
Figure 8.15 This wound has penetrated the stifle joint and a trickle of leaking synovial fluid can be seen
What happens when bacteria invade a joint?
Bacteria colonize the synovial membrane and cause an acute inflammatory response. This
leads to the release of enzymes that can damage the articular cartilage. Ultimately, the
cartilage may be completely eroded so the infection invades the subchondral bone resulting