Page 34 - Financial Statement Analysis
P. 34
sub79433_ch01.qxd 4/7/08 11:20 AM Page 11
Chapter One | Overview of Financial Statement Analysis 11
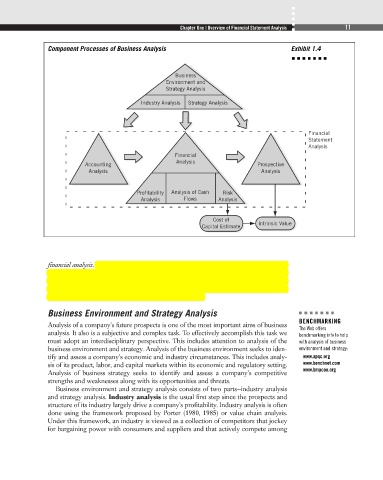
Component Processes of Business Analysis Exhibit 1.4
Business
Environment and
Strategy Analysis
Industry Analysis Strategy Analysis
Financial
Statement
Analysis
Financial
Analysis
Accounting Prospective
Analysis Analysis
Profitability Analysis of Cash Risk
Analysis Flows Analysis
Cost of
Capital Estimate Intrinsic Value
financial analysis. In turn, the quality of financial analysis depends on the reliability and
economic content of the financial statements. This requires accounting analysis of finan-
cial statements. Financial statement analysis involves all of these component processes—
accounting, financial, and prospective analyses. This section discusses each of these
component processes in the context of business analysis.
Business Environment and Strategy Analysis
BENCHMARKING
Analysis of a company’s future prospects is one of the most important aims of business The Web offers
analysis. It also is a subjective and complex task. To effectively accomplish this task we benchmarking info to help
must adopt an interdisciplinary perspective. This includes attention to analysis of the with analysis of business
business environment and strategy. Analysis of the business environment seeks to iden- environment and strategy:
tify and assess a company’s economic and industry circumstances. This includes analy- www.apqc.org
sis of its product, labor, and capital markets within its economic and regulatory setting. www.benchnet.com
Analysis of business strategy seeks to identify and assess a company’s competitive www.bmpcoe.org
strengths and weaknesses along with its opportunities and threats.
Business environment and strategy analysis consists of two parts—industry analysis
and strategy analysis. Industry analysis is the usual first step since the prospects and
structure of its industry largely drive a company’s profitability. Industry analysis is often
done using the framework proposed by Porter (1980, 1985) or value chain analysis.
Under this framework, an industry is viewed as a collection of competitors that jockey
for bargaining power with consumers and suppliers and that actively compete among