Page 12 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 12
Nutrients 3
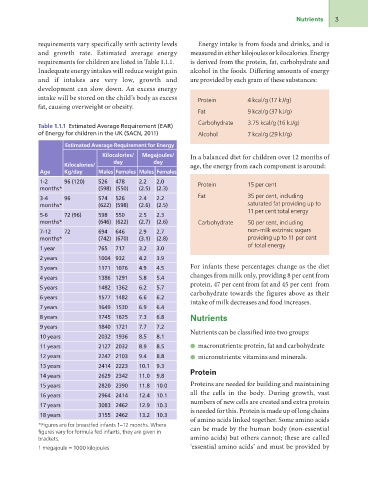
requirements vary specifically with activity levels Energy intake is from foods and drinks, and is
and growth rate. Estimated average energy measured in either kilojoules or kilocalories. Energy
requirements for children are listed in Table 1.1.1. is derived from the protein, fat, carbohydrate and
Inadequate energy intakes will reduce weight gain alcohol in the foods. Differing amounts of energy
and if intakes are very low, growth and are provided by each gram of these substances:
development can slow down. An excess energy
intake will be stored on the child’s body as excess Protein 4 kcal/g (17 kJ/g)
fat, causing overweight or obesity. Fat 9 kcal/g (37 kJ/g)
Carbohydrate 3.75 kcal/g (16 kJ/g)
Table 1.1.1 Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) Alcohol 7 kcal/g (29 kJ/g)
of Energy for children in the UK (SACN, 2011)
Estimated Average Requirement for Energy
Kilocalories/ Megajoules/ In a balanced diet for children over 12 months of
age, the energy from each component is around:
Kilocalories/ day day
Age Kg/day Males Females Males Females
1-2 96 (120) 526 478 2.2 2.0 Protein 15 per cent
months* (598) (550) (2.5) (2.3)
3-4 96 574 526 2.4 2.2 Fat 35 per cent, including
months* (622) (598) (2.6) (2.5) saturated fat providing up to
11 per cent total energy
5-6 72 (96) 598 550 2.5 2.3
months* (646) (622) (2.7) (2.6) Carbohydrate 50 per cent, including
non-milk extrinsic sugars
7-12 72 694 646 2.9 2.7 providing up to 11 per cent
months* (742) (670) (3.1) (2.8) of total energy
1 year 765 717 3.2 3.0
2 years 1004 932 4.2 3.9
3 years 1171 1076 4.9 4.5 For infants these percentages change as the diet
changes from milk only, providing 8 per cent from
4 years 1386 1291 5.8 5.4 protein, 47 per cent from fat and 45 per cent from
carbohydrate towards the figures above as their
5 years 1482 1362 6.2 5.7 intake of milk decreases and food increases.
6 years 1577 1482 6.6 6.2 Nutrients
7 years 1649 1530 6.9 6.4 Nutrients can be classified into two groups:
8 years 1745 1625 7.3 6.8 ●● macronutrients: protein, fat and carbohydrate
9 years 1840 1721 7.7 7.2 ●● micronutrients: vitamins and minerals.
10 years 2032 1936 8.5 8.1 Protein
11 years 2127 2032 8.9 8.5 Proteins are needed for building and maintaining
all the cells in the body. During growth, vast
12 years 2247 2103 9.4 8.8 numbers of new cells are created and extra protein
is needed for this. Protein is made up of long chains
13 years 2414 2223 10.1 9.3 of amino acids linked together. Some amino acids
can be made by the human body (non-essential
14 years 2629 2342 11.0 9.8 amino acids) but others cannot; these are called
‘essential amino acids’ and must be provided by
15 years 2820 2390 11.8 10.0
16 years 2964 2414 12.4 10.1
17 years 3083 2462 12.9 10.3
18 years 3155 2462 13.2 10.3
*Figures are for breastfed infants 1–12 months. Where
figures vary for formula fed infants, they are given in
brackets.
1 megajoule = 1000 kilojoules