Page 75 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 75
66 3.2 Pregnancy
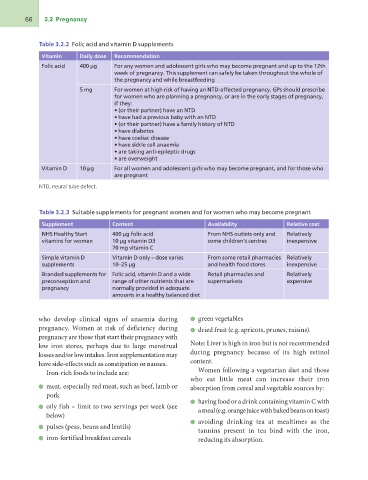
Table 3.2.2 Folic acid and vitamin D supplements
Vitamin Daily dose Recommendation
Folic acid 400 µg
5 mg For any women and adolescent girls who may become pregnant and up to the 12th
Vitamin D week of pregnancy. This supplement can safely be taken throughout the whole of
10 µg the pregnancy and while breastfeeding
For women at high risk of having an NTD-affected pregnancy. GPs should prescribe
for women who are planning a pregnancy, or are in the early stages of pregnancy,
if they:
• (or their partner) have an NTD
• have had a previous baby with an NTD
• (or their partner) have a family history of NTD
• have diabetes
• have coeliac disease
• have sickle cell anaemia
• are taking anti-epileptic drugs
• are overweight
For all women and adolescent girls who may become pregnant, and for those who
are pregnant
NTD, neural tube defect.
Table 3.2.3 Suitable supplements for pregnant women and for women who may become pregnant
Supplement Content Availability Relative cost
NHS Healthy Start 400 µg folic acid From NHS outlets only and Relatively
vitamins for women 10 µg vitamin D3 some children’s centres inexpensive
70 mg vitamin C
Simple vitamin D From some retail pharmacies Relatively
supplements Vitamin D only – dose varies and health food stores inexpensive
10–25 µg
Branded supplements for Retail pharmacies and Relatively
preconception and Folic acid, vitamin D and a wide supermarkets expensive
pregnancy range of other nutrients that are
normally provided in adequate
amounts in a healthy balanced diet
who develop clinical signs of anaemia during ●● green vegetables
pregnancy. Women at risk of deficiency during
pregnancy are those that start their pregnancy with ●● dried fruit (e.g. apricots, prunes, raisins).
low iron stores, perhaps due to large menstrual
losses and/or low intakes. Iron supplementation may Note: Liver is high in iron but is not recommended
have side-effects such as constipation or nausea. during pregnancy because of its high retinol
content.
Iron-rich foods to include are:
Women following a vegetarian diet and those
●● meat, especially red meat, such as beef, lamb or who eat little meat can increase their iron
pork absorption from cereal and vegetable sources by:
●● oily fish – limit to two servings per week (see ●● having food or a drink containing vitamin C with
below) a meal (e.g. orange juice with baked beans on toast)
●● pulses (peas, beans and lentils) ●● avoiding drinking tea at mealtimes as the
tannins present in tea bind with the iron,
●● iron-fortified breakfast cereals reducing its absorption.