Page 77 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 77
68 3.2 Pregnancy
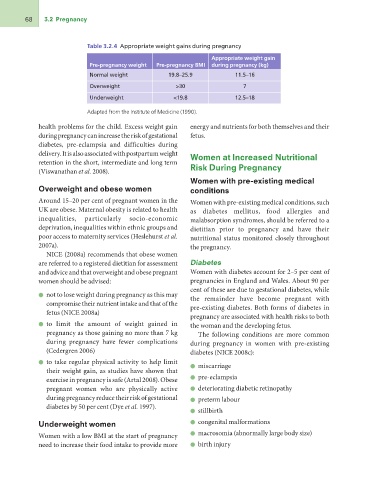
Table 3.2.4 Appropriate weight gains during pregnancy
Pre-pregnancy weight Pre-pregnancy BMI Appropriate weight gain
Normal weight 19.8–25.9 during pregnancy (kg)
11.5–16
Overweight >30 7
Underweight <19.8 12.5–18
Adapted from the Institute of Medicine (1990).
health problems for the child. Excess weight gain energy and nutrients for both themselves and their
during pregnancy can increase the risk of gestational fetus.
diabetes, pre-eclampsia and difficulties during
delivery. It is also associated with postpartum weight Women at Increased Nutritional
retention in the short, intermediate and long term Risk During Pregnancy
(Viswanathan et al. 2008).
Women with pre-existing medical
Overweight and obese women conditions
Around 15–20 per cent of pregnant women in the Women with pre-existing medical conditions, such
UK are obese. Maternal obesity is related to health as diabetes mellitus, food allergies and
inequalities, particularly socio-economic malabsorption syndromes, should be referred to a
deprivation, inequalities within ethnic groups and dietitian prior to pregnancy and have their
poor access to maternity services (Heslehurst et al. nutritional status monitored closely throughout
2007a). the pregnancy.
NICE (2008a) recommends that obese women Diabetes
are referred to a registered dietitian for assessment Women with diabetes account for 2–5 per cent of
and advice and that overweight and obese pregnant pregnancies in England and Wales. About 90 per
women should be advised: cent of these are due to gestational diabetes, while
the remainder have become pregnant with
●● not to lose weight during pregnancy as this may pre-existing diabetes. Both forms of diabetes in
compromise their nutrient intake and that of the pregnancy are associated with health risks to both
fetus (NICE 2008a) the woman and the developing fetus.
●● to limit the amount of weight gained in The following conditions are more common
pregnancy as those gaining no more than 7 kg during pregnancy in women with pre-existing
during pregnancy have fewer complications diabetes (NICE 2008c):
(Cedergren 2006)
●● miscarriage
●● to take regular physical activity to help limit
their weight gain, as studies have shown that ●● pre-eclampsia
exercise in pregnancy is safe (Artal 2008). Obese
pregnant women who are physically active ●● deteriorating diabetic retinopathy
during pregnancy reduce their risk of gestational
diabetes by 50 per cent (Dye et al. 1997). ●● preterm labour
Underweight women ●● stillbirth
Women with a low BMI at the start of pregnancy ●● congenital malformations
need to increase their food intake to provide more
●● macrosomia (abnormally large body size)
●● birth injury