Page 41 - ABCTE Study Guide_Neat
P. 41
Suffixes can indicate whether a word is a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb. They can also modify and
extend meaning.
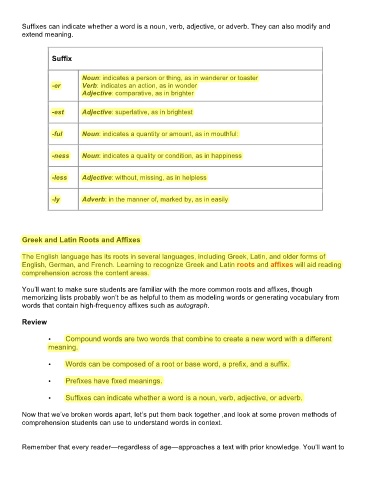
Suffix
Noun: indicates a person or thing, as in wanderer or toaster
-er Verb: indicates an action, as in wonder
Adjective: comparative, as in brighter
-est Adjective: superlative, as in brightest
-ful Noun: indicates a quantity or amount, as in mouthful:
-ness Noun: indicates a quality or condition, as in happiness
-less Adjective: without, missing, as in helpless
-ly Adverb: in the manner of, marked by, as in easily
Greek and Latin Roots and Affixes
The English language has its roots in several languages, including Greek, Latin, and older forms of
English, German, and French. Learning to recognize Greek and Latin roots and affixes will aid reading
comprehension across the content areas.
You’ll want to make sure students are familiar with the more common roots and affixes, though
memorizing lists probably won’t be as helpful to them as modeling words or generating vocabulary from
words that contain high-frequency affixes such as autograph.
Review
• Compound words are two words that combine to create a new word with a different
meaning.
• Words can be composed of a root or base word, a prefix, and a suffix.
• Prefixes have fixed meanings.
• Suffixes can indicate whether a word is a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb.
Now that we’ve broken words apart, let’s put them back together ,and look at some proven methods of
comprehension students can use to understand words in context.
Remember that every reader—regardless of age—approaches a text with prior knowledge. You’ll want to