Page 69 - ABCTE Study Guide_Neat
P. 69
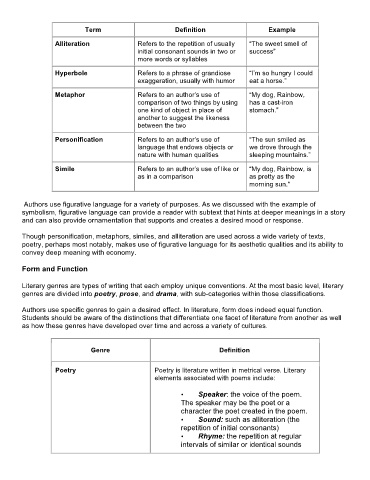
Term Definition Example
Alliteration Refers to the repetition of usually “The sweet smell of
initial consonant sounds in two or success”
more words or syllables
Hyperbole Refers to a phrase of grandiose “I’m so hungry I could
exaggeration, usually with humor eat a horse.”
Metaphor Refers to an author’s use of “My dog, Rainbow,
comparison of two things by using has a cast-iron
one kind of object in place of stomach.”
another to suggest the likeness
between the two
Personification Refers to an author’s use of “The sun smiled as
language that endows objects or we drove through the
nature with human qualities sleeping mountains.”
Simile Refers to an author’s use of like or “My dog, Rainbow, is
as in a comparison as pretty as the
morning sun."
Authors use figurative language for a variety of purposes. As we discussed with the example of
symbolism, figurative language can provide a reader with subtext that hints at deeper meanings in a story
and can also provide ornamentation that supports and creates a desired mood or response.
Though personification, metaphors, similes, and alliteration are used across a wide variety of texts,
poetry, perhaps most notably, makes use of figurative language for its aesthetic qualities and its ability to
convey deep meaning with economy.
Form and Function
Literary genres are types of writing that each employ unique conventions. At the most basic level, literary
genres are divided into poetry, prose, and drama, with sub-categories within those classifications.
Authors use specific genres to gain a desired effect. In literature, form does indeed equal function.
Students should be aware of the distinctions that differentiate one facet of literature from another as well
as how these genres have developed over time and across a variety of cultures.
Genre Definition
Poetry Poetry is literature written in metrical verse. Literary
elements associated with poems include:
• Speaker: the voice of the poem.
The speaker may be the poet or a
character the poet created in the poem.
• Sound: such as alliteration (the
repetition of initial consonants)
• Rhyme: the repetition at regular
intervals of similar or identical sounds