Page 74 - ABCTE Study Guide_Neat
P. 74
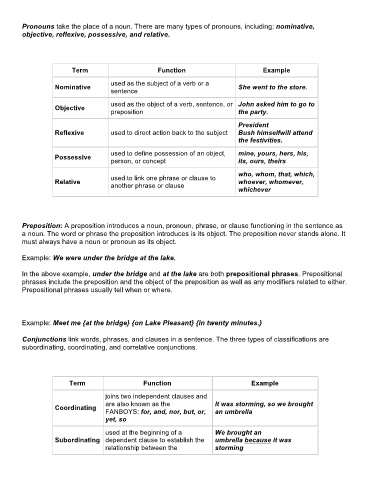
Pronouns take the place of a noun. There are many types of pronouns, including: nominative,
objective, reflexive, possessive, and relative.
Term Function Example
used as the subject of a verb or a
Nominative She went to the store.
sentence
used as the object of a verb, sentence, or John asked him to go to
Objective
preposition the party.
President
Reflexive used to direct action back to the subject Bush himselfwill attend
the festivities.
used to define possession of an object, mine, yours, hers, his,
Possessive
person, or concept its, ours, theirs
who, whom, that, which,
used to link one phrase or clause to
Relative whoever, whomever,
another phrase or clause
whichever
Preposition: A preposition introduces a noun, pronoun, phrase, or clause functioning in the sentence as
a noun. The word or phrase the preposition introduces is its object. The preposition never stands alone. It
must always have a noun or pronoun as its object.
Example: We were under the bridge at the lake.
In the above example, under the bridge and at the lake are both prepositional phrases. Prepositional
phrases include the preposition and the object of the preposition as well as any modifiers related to either.
Prepositional phrases usually tell when or where.
Example: Meet me {at the bridge} {on Lake Pleasant} {in twenty minutes.}
Conjunctions link words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. The three types of classifications are
subordinating, coordinating, and correlative conjunctions.
Term Function Example
joins two independent clauses and
are also known as the It was storming, so we brought
Coordinating
FANBOYS: for, and, nor, but, or, an umbrella
yet, so
used at the beginning of a We brought an
Subordinating dependent clause to establish the umbrella because it was
relationship between the storming