Page 135 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 135
2.7
Drug Metabolism
1. Heroin is a synthetic derivative of the naturally occurring opioid analgesic morphine. Given its illicit
morphine. Which phase I transformation is responsible for the conversion of heroin to morphine?
Heroin
Morphine
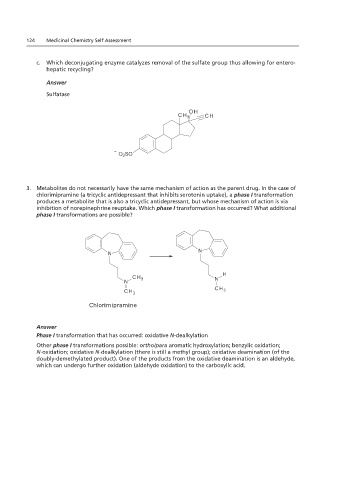
2. Estradiol, the estrogen component of many oral contraceptives, undergoes a phase II conjugation then
reabsorbed (at least in part). Consider the structure of estradiol drawn below and do the following:
a. Modify the structure drawn below to show the product of a sulfate conjugation (phase II
transformation).
124 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
b. Which enzyme is required to make this sulfate conjugate?
Answer: Sulfotransferase (SULT)
c. Which deconjugating enzyme catalyzes removal of the sulfate group thus allowing for entero-
hepatic recycling?
c. Which deconjugating enzyme catalyzes removal of the sulfate group thus allowing for
enterohepatic recycling?
Answer
Sulfatase
Answer: Sulfatase
-
3. Metabolites do not necessarily have the same mechanism of action as the parent drug. In the case of
chlorimipramine (a tricyclic antidepressant that inhibits serotonin uptake), a phase I transformation
produces a metabolite that is also a tricyclic antidepressant, but whose mechanism of action is via
inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake. Which phase I transformation has occurred? What additional
phase I transformations are possible?
3. Metabolites do not. In the case of I transformations are possible?
Chlorimipramine
Answer
4. Evaluate each of the which phase I metabolic transformation has occurred.
Phase I transformation that has occurred: oxidative N-dealkylation
H
Other phase I transformations possible: ortho/para aromatic hydroxylation; benzylic oxidation;
N-oxidation; oxidative N-dealkylation (there is still a methyl group); oxidative deamination (of the
N
C H
NH
3
2
doubly-demethylated product). One of the products from the oxidative deamination is an aldehyde,
which can undergo further oxidation (aldehyde oxidation) to the carboxylic acid.
CH 3 CH 3
CF 3 CF 3
Dexfenfluramine
Fluvoxamine
H 2 N O CO 2 H O
OH OH
Cl Cl
Baclofen