Page 67 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 67
A A B C B C D D E F E F
1. Using the
1. Using the
2. Based on or induction.
2. Based on or induction.
3. Using the.4, and 8.5. E
3. Using the.4, and 8.5.
C D
56 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
A
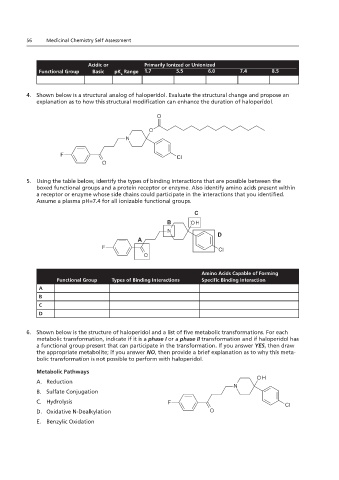
Acidic or Primarily Ionized or Unionized
F
Functional Group Basic pK Range 1.7 5.5 6.0 7.4 8.5
a B
1. Using the
4. Shown below modification can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
4. Shown below is a structural analog of haloperidol. Evaluate the structural change and propose an
explanation as to how this structural modification can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
2. Based on or induction.
4. Shown below modification can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
3. Using the.4, and 8.5.
5. Using the table below, identify the groups.
5. Using the table below, identify the types of binding interactions that are possible between the
boxed functional groups and a protein receptor or enzyme. Also identify amino acids present within
4. Shown below modification can enhance the duration of haloperidol.
a receptor or enzyme whose side chains could participate in the interactions that you identified.
5. Using the table below, identify the groups.
Assume a plasma pH=7.4 for all ionizable functional groups.
C
B C
B D
A
D
A
6. Shown below is the perform with haloperidol.
6. Shown below is the perform with haloperidol. Amino Acids Capable of Forming
5. Using the table below, identify the groups.
Specific Binding Interaction
Types of Binding Interactions
Functional Group
A
B C
C B
D
D
A
6. Shown below is the structure of haloperidol and a list of five metabolic transformations. For each
metabolic transformation, indicate if it is a phase I or a phase II transformation and if haloperidol has
a functional group present that can participate in the transformation. If you answer YES, then draw
the appropriate metabolite; if you answer NO, then provide a brief explanation as to why this meta-
bolic transformation is not possible to perform with haloperidol.
6. Shown below is the perform with haloperidol.
Metabolic Pathways
A. Reduction
B. Sulfate Conjugation
C. Hydrolysis
D. Oxidative N-Dealkylation
E. Benzylic Oxidation