Page 132 - IGC BOOK
P. 132
Closing the Audit
The purpose of the audit report is to communicate the results of the audit outcomes. The report
should provide correct and clear data that will be effective as a management aid in addressing
important organizational issues. The audit process may end when the report is issued by the
lead auditor or after follow-up actions are completed.
Requests for correcting nonconformities or findings within audits are very common.
• Corrective action is action taken to eliminate the causes of an existing nonconformity,
defect, or other undesirable situation in order to prevent recurrence (reactive). Corrective
action is about eliminating the causes of problems and not just following a series of problem-
solving steps.
• Preventive action is action taken to eliminate the causes of a potential nonconformity,
defect, or other undesirable situation in order to prevent occurrence (proactive).
Audit Records
The organisation should establish and maintain audit records consistent with the safety and
health management system records. Their retention times should be established and should
comply with legal requirements.
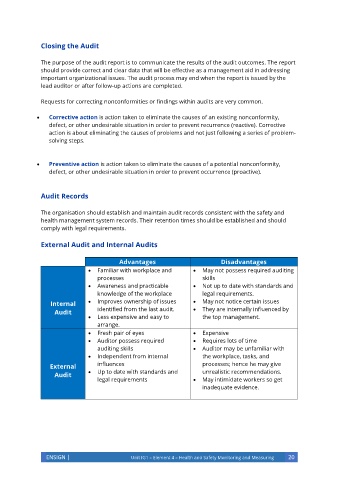
External Audit and Internal Audits
Advantages Disadvantages
• Familiar with workplace and • May not possess required auditing
processes skills
• Awareness and practicable • Not up to date with standards and
knowledge of the workplace legal requirements.
Internal • Improves ownership of issues • May not notice certain issues
Audit identified from the last audit. • They are internally influenced by
• Less expensive and easy to the top management.
arrange.
• Fresh pair of eyes • Expensive
• Auditor possess required • Requires lots of time
auditing skills • Auditor may be unfamiliar with
• Independent from internal the workplace, tasks, and
External influences processes; hence he may give
Audit • Up to date with standards and unrealistic recommendations.
legal requirements • May intimidate workers so get
inadequate evidence.
ENSIGN | Unit IG1 – Element 4 – Health and Safety Monitoring and Measuring 20