Page 211 - IGC BOOK
P. 211
Assessment of Health Risks 7.2
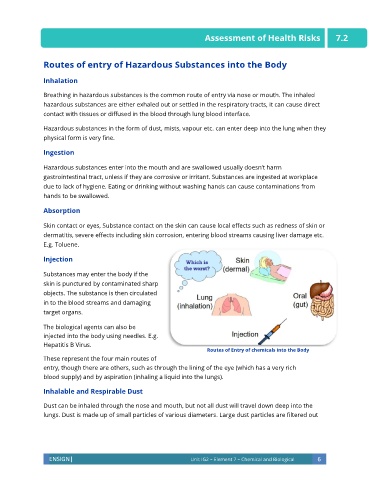
Routes of entry of Hazardous Substances into the Body
Inhalation
Breathing in hazardous substances is the common route of entry via nose or mouth. The inhaled
hazardous substances are either exhaled out or settled in the respiratory tracts, it can cause direct
contact with tissues or diffused in the blood through lung blood interface.
Hazardous substances in the form of dust, mists, vapour etc. can enter deep into the lung when they
physical form is very fine.
Ingestion
Hazardous substances enter into the mouth and are swallowed usually doesn’t harm
gastrointestinal tract, unless if they are corrosive or irritant. Substances are ingested at workplace
due to lack of hygiene. Eating or drinking without washing hands can cause contaminations from
hands to be swallowed.
Absorption
Skin contact or eyes, Substance contact on the skin can cause local effects such as redness of skin or
dermatitis, severe effects including skin corrosion, entering blood streams causing liver damage etc.
E.g. Toluene.
Injection
Substances may enter the body if the
skin is punctured by contaminated sharp
objects. The substance is then circulated
in to the blood streams and damaging
target organs.
The biological agents can also be
injected into the body using needles. E.g.
Hepatitis B Virus.
Routes of Entry of chemicals into the Body
These represent the four main routes of
entry, though there are others, such as through the lining of the eye (which has a very rich
blood supply) and by aspiration (inhaling a liquid into the lungs).
Inhalable and Respirable Dust
Dust can be inhaled through the nose and mouth, but not all dust will travel down deep into the
lungs. Dust is made up of small particles of various diameters. Large dust particles are filtered out
ENSIGN| Unit IG2 – Element 7 – Chemical and Biological 6
Agents