Page 5 - PG 101-Course notes مذكرة النظري 24-25 with spec
P. 5
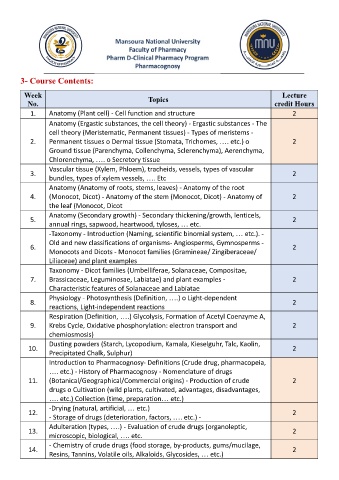
3- Course Contents:
Week Topics Lecture
No. credit Hours
1. Anatomy (Plant cell) - Cell function and structure 2
Anatomy (Ergastic substances, the cell theory) - Ergastic substances - The
cell theory (Meristematic, Permanent tissues) - Types of meristems -
2. Permanent tissues o Dermal tissue (Stomata, Trichomes, …. etc.) o 2
Ground tissue (Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma), Aerenchyma,
Chlorenchyma, …. o Secretory tissue
Vascular tissue (Xylem, Phloem), tracheids, vessels, types of vascular
3. 2
bundles, types of xylem vessels, …. Etc
Anatomy (Anatomy of roots, stems, leaves) - Anatomy of the root
4. (Monocot, Dicot) - Anatomy of the stem (Monocot, Dicot) - Anatomy of 2
the leaf (Monocot, Dicot
Anatomy (Secondary growth) - Secondary thickening/growth, lenticels,
5. 2
annual rings, sapwood, heartwood, tyloses, … etc.
-Taxonomy - Introduction (Naming, scientific binomial system, … etc.). -
Old and new classifications of organisms- Angiosperms, Gymnosperms -
6. 2
Monocots and Dicots - Monocot families (Gramineae/ Zingiberaceae/
Liliaceae) and plant examples
Taxonomy - Dicot families (Umbelliferae, Solanaceae, Compositae,
7. Brassicaceae, Leguminosae, Labiatae) and plant examples - 2
Characteristic features of Solanaceae and Labiatae
Physiology - Photosynthesis (Definition, ….) o Light-dependent
8. 2
reactions, Light-independent reactions
Respiration (Definition, ….) Glycolysis, Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A,
9. Krebs Cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and 2
chemiosmosis)
Dusting powders (Starch, Lycopodium, Kamala, Kieselguhr, Talc, Kaolin,
10. 2
Precipitated Chalk, Sulphur)
Introduction to Pharmacognosy- Definitions (Crude drug, pharmacopeia,
…. etc.) - History of Pharmacognosy - Nomenclature of drugs
11. (Botanical/Geographical/Commercial origins) - Production of crude 2
drugs o Cultivation (wild plants, cultivated, advantages, disadvantages,
…. etc.) Collection (time, preparation… etc.)
-Drying (natural, artificial, … etc.)
12. 2
- Storage of drugs (deterioration, factors, …. etc.) -
Adulteration (types, ….) - Evaluation of crude drugs (organoleptic,
13. 2
microscopic, biological, …. etc.
- Chemistry of crude drugs (food storage, by-products, gums/mucilage,
14. 2
Resins, Tannins, Volatile oils, Alkaloids, Glycosides, … etc.)