Page 27 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 27
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
A) Monosaccharide:
• They are crystalline water-soluble substances with sweet taste.
• By hydrolysis they cannot yield simpler sugars; e.g., glucose, galactose.
• They are the simplest sugars and can be defined as polyhydroxyaldehydes
or polyhydroxyketones with at least three aliphatic carbon atoms.
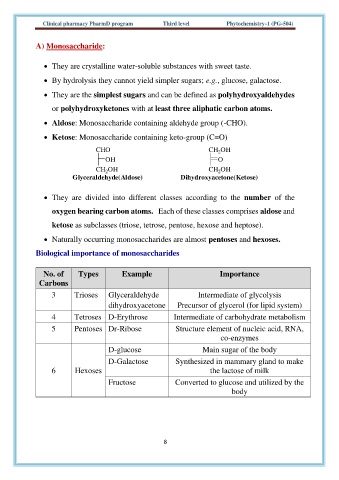
• Aldose: Monosaccharide containing aldehyde group (-CHO).
• Ketose: Monosaccharide containing keto-group (C=O)
CHO CH OH
2
OH O
CH OH CH OH
2
2
Glyceraldehyde(Aldose) Dihydroxyacetone(Ketose)
• They are divided into different classes according to the number of the
oxygen bearing carbon atoms. Each of these classes comprises aldose and
ketose as subclasses (triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose and heptose).
• Naturally occurring monosaccharides are almost pentoses and hexoses.
Biological importance of monosaccharides
No. of Types Example Importance
Carbons
3 Trioses Glyceraldehyde Intermediate of glycolysis
dihydroxyacetone Precursor of glycerol (for lipid system)
4 Tetroses D-Erythrose Intermediate of carbohydrate metabolism
5 Pentoses Dr-Ribose Structure element of nucleic acid, RNA,
co-enzymes
D-glucose Main sugar of the body
D-Galactose Synthesized in mammary gland to make
6 Hexoses the lactose of milk
Fructose Converted to glucose and utilized by the
body
8