Page 35 - Pharmacognosy 2 PG303 (1)
P. 35
Pharmacognosy-2 (PG303) Level 2 Clinical Pharmacy-Pharm D
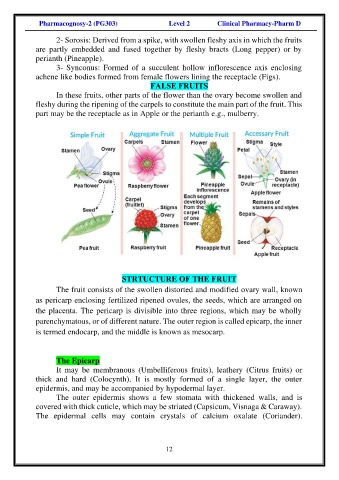
2- Sorosis: Derived from a spike, with swollen fleshy axis in which the fruits
are partly embedded and fused together by fleshy bracts (Long pepper) or by
perianth (Pineapple).
3- Synconus: Formed of a succulent hollow inflorescence axis enclosing
achene like bodies formed from female flowers lining the receptacle (Figs).
FALSE FRUITS
In these fruits, other parts of the flower than the ovary become swollen and
fleshy during the ripening of the carpels to constitute the main part of the fruit. This
part may be the receptacle as in Apple or the perianth e.g., mulberry.
STRTUCTURE OF THE FRUIT
The fruit consists of the swollen distorted and modified ovary wall, known
as pericarp enclosing fertilized ripened ovules, the seeds, which are arranged on
the placenta. The pericarp is divisible into three regions, which may be wholly
parenchymatous, or of different nature. The outer region is called epicarp, the inner
is termed endocarp, and the middle is known as mesocarp.
The Epicarp
It may be membranous (Umbelliferous fruits), leathery (Citrus fruits) or
thick and hard (Colocynth). It is mostly formed of a single layer, the outer
epidermis, and may be accompanied by hypodermal layer.
The outer epidermis shows a few stomata with thickened walls, and is
covered with thick cuticle, which may be striated (Capsicum, Visnaga & Caraway).
The epidermal cells may contain crystals of calcium oxalate (Coriander).
12