Page 17 - Data Science Algorithms in a Week
P. 17
2 Ramazan Ünlü
INTRODUCTION
Data mining (DM) is one of the most notable research areas in the last decades. DM
can be defined as interdisciplinary area of an intersection of Artificial Intelligence (AI),
machine learning, and statistics. One of the earliest studies of the DM, which highlights
some of its distinctive characteristics, is proposed by (Fayyad, Piatetsky-Shapiro, &
Smyth, 1996; Kantardzic, 2011), who define it as "the nontrivial process of identifying
valid, novel, potentially useful, and ultimately understandable patterns in data.". In
general, the process of extraction of implicit, hidden, and potentially useful knowledge
from data is a well-accepted definition of DM.
With the growing use of computers and data storage technology, there exists a great
amount of data being produced by different systems. Data can be defined as a set of
qualitative or quantitative variables such as facts, numbers, or texts that describe the
things. For DM, the standard structure of a data is a collection of samples in which
measurements named features are specified, and these features are obtained in many
cases. If we consider that a sample is represented by a multidimensional vector, each
dimension can be considered as one feature of the sample. In other words, it can be said
that features are some values that represent the specific characteristic of a sample
(Kantardzic, 2011).
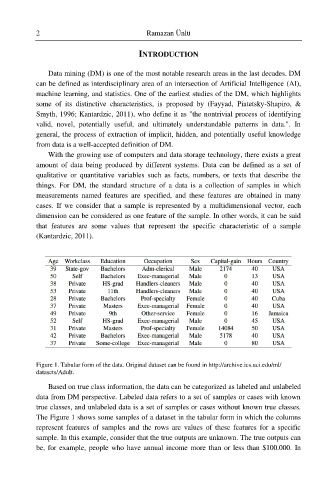
Figure 1. Tabular form of the data. Original dataset can be found in http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/
datasets/Adult.
Based on true class information, the data can be categorized as labeled and unlabeled
data from DM perspective. Labeled data refers to a set of samples or cases with known
true classes, and unlabeled data is a set of samples or cases without known true classes.
The Figure 1 shows some samples of a dataset in the tabular form in which the columns
represent features of samples and the rows are values of these features for a specific
sample. In this example, consider that the true outputs are unknown. The true outputs can
be, for example, people who have annual income more than or less than $100.000. In