Page 62 - Data Science Algorithms in a Week
P. 62
Naive Bayes
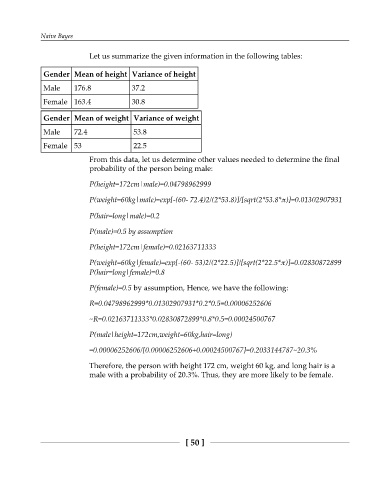
Let us summarize the given information in the following tables:
Gender Mean of height Variance of height
Male 176.8 37.2
Female 163.4 30.8
Gender Mean of weight Variance of weight
Male 72.4 53.8
Female 53 22.5
From this data, let us determine other values needed to determine the final
probability of the person being male:
P(height=172cm|male)=0.04798962999
P(weight=60kg|male)=exp[-(60- 72.4)2/(2*53.8)]/[sqrt(2*53.8*π)]=0.01302907931
P(hair=long|male)=0.2
P(male)=0.5 by assumption
P(height=172cm|female)=0.02163711333
P(weight=60kg|female)=exp[-(60- 53)2/(2*22.5)]/[sqrt(2*22.5*π)]=0.02830872899
P(hair=long|female)=0.8
P(female)=0.5 by assumption, Hence, we have the following:
R=0.04798962999*0.01302907931*0.2*0.5=0.00006252606
~R=0.02163711333*0.02830872899*0.8*0.5=0.00024500767
P(male|height=172cm,weight=60kg,hair=long)
=0.00006252606/[0.00006252606+0.00024500767]=0.2033144787~20.3%
Therefore, the person with height 172 cm, weight 60 kg, and long hair is a
male with a probability of 20.3%. Thus, they are more likely to be female.
[ 50 ]