Page 10 - Module 1-Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone Function Final (Interactive)
P. 10
Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone
Anterior pituitary lobe
In contrast to the posterior pituitary, the anterior pituitary does manufacture
hormones. These hormones are regulated primarily by “releasing hormones”
secreted by the hypothalamus.
Anterior lobe hormones
As you can see from Table 2, the anterior lobe of the pituitary produces several
hormones.
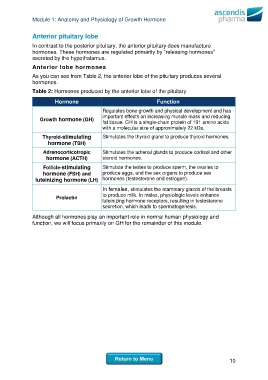
Table 2: Hormones produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary
Hormone Function
Regulates bone growth and physical development and has
important effects on increasing muscle mass and reducing
Growth hormone (GH)
fat tissue. GH is a single-chain protein of 191 amino acids
with a molecular size of approximately 22 kDa.
Thyroid-stimulating Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones.
hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic Stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other
hormone (ACTH) steroid hormones.
Follicle-stimulating Stimulate the testes to produce sperm, the ovaries to
hormone (FSH) and produce eggs, and the sex organs to produce sex
luteinizing hormone (LH) hormones (testosterone and estrogen).
In females, stimulates the mammary glands of the breasts
to produce milk. In males, physiologic levels enhance
Prolactin
luteinizing hormone receptors, resulting in testosterone
secretion, which leads to spermatogenesis.
Although all hormones play an important role in normal human physiology and
function, we will focus primarily on GH for the remainder of this module.
10