Page 16 - Module 1-Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone Function Final (Interactive)
P. 16
Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone
Growth hormone and energy balance
The relationship between GH and the stomach is related to ghrelin and leptin.
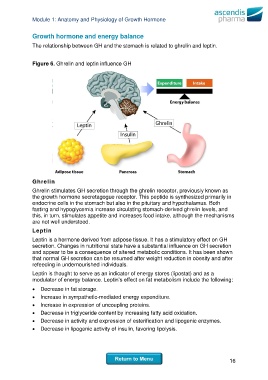
Figure 6. Ghrelin and leptin influence GH
Ghrelin
Ghrelin stimulates GH secretion through the ghrelin receptor, previously known as
the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. This peptide is synthesized primarily in
endocrine cells in the stomach but also in the pituitary and hypothalamus. Both
fasting and hypoglycemia increase circulating stomach-derived ghrelin levels, and
this, in turn, stimulates appetite and increases food intake, although the mechanisms
are not well understood.
Leptin
Leptin is a hormone derived from adipose tissue. It has a stimulatory effect on GH
secretion. Changes in nutritional state have a substantial influence on GH secretion
and appear to be a consequence of altered metabolic conditions. It has been shown
that normal GH secretion can be resumed after weight reduction in obesity and after
refeeding in undernourished individuals.
Leptin is thought to serve as an indicator of energy stores (lipostat) and as a
modulator of energy balance. Leptin’s effect on fat metabolism include the following:
• Decrease in fat storage.
• Increase in sympathetic-mediated energy expenditure.
• Increase in expression of uncoupling proteins.
• Decrease in triglyceride content by increasing fatty acid oxidation.
• Decrease in activity and expression of esterification and lipogenic enzymes.
• Decrease in lipogenic activity of insulin, favoring lipolysis.
16