Page 21 - Module 1-Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone Function Final (Interactive)
P. 21
Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone
Factors that Affect GH Action
Factors such as age, gender, and body composition may have an effect on GH
activity as well.
Age
GH has an influence on the body from birth through puberty until adulthood. In
normal adults, the decline in GH levels with age is accompanied by a decline in
serum IGF-1 levels.
• Longitudinal bone growth is stimulated by GH directly on the growth plate, IGF-1
produced locally in the growth plate in response to GH and by circulating IGF-1.
During puberty, there can be a 1.5- to 3-fold increase in the pulsatile secretion of
GH and a more than 3-fold increase in the concentration of serum IGF-1.
It has also been shown that the breakdown in fat in response to GH administration
appears to be higher in younger as compared to older subjects, in part because of
differences in the amount of abdominal fat.
Gender
Both boys and girls increase their GH and IGF-1 output during puberty, but there are
changes in body composition that are gender-specific:
• The larger skeletal muscle mass in males is the result of androgenic hormones
and a greater sensitivity to GH and IGF-1 produced as compared with females.
• Gender differences are also influenced by the earlier timing and completion of
puberty in the female.
Females actually produce more GH than males and this difference is apparent even
in puberty. However, despite the higher output of GH output in normal females, adult
females receiving GH may be less sensitive to the metabolic effects of GH than
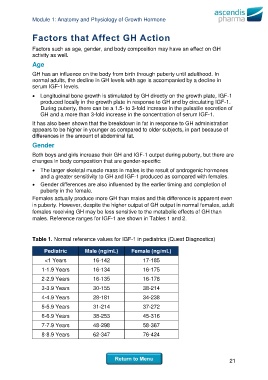
males. Reference ranges for IGF-1 are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1. Normal reference values for IGF-1 in pediatrics (Quest Diagnostics)
Pediatric Male (ng/mL) Female (ng/mL)
<1 Years 16-142 17-185
1-1.9 Years 16-134 16-175
2-2.9 Years 16-135 16-178
3-3.9 Years 30-155 38-214
4-4.9 Years 28-181 34-238
5-5.9 Years 31-214 37-272
6-6.9 Years 38-253 45-316
7-7.9 Years 48-298 58-367
8-8.9 Years 62-347 76-424
21