Page 24 - Module 1-Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone Function Final (Interactive)
P. 24
Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of Growth Hormone
Metabolic Effects of GH
GH signaling
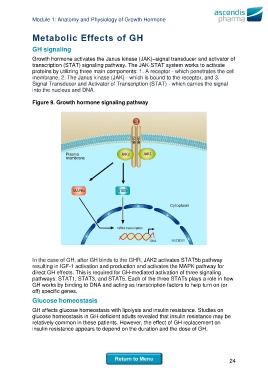
Growth hormone activates the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of
transcription (STAT) signaling pathway. The JAK-STAT system works to activate
proteins by utilizing three main components: 1. A receptor - which penetrates the cell
membrane, 2. The Janus kinase (JAK) - which is bound to the receptor, and 3.
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) - which carries the signal
into the nucleus and DNA.
Figure 9. Growth hormone signaling pathway
In the case of GH, after GH binds to the GHR, JAK2 activates STAT5b pathway
resulting in IGF-1 activation and production and activates the MAPK pathway for
direct GH effects. This is required for GH-mediated activation of three signaling
pathways: STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5. Each of the three STATs plays a role in how
GH works by binding to DNA and acting as transcription factors to help turn on (or
off) specific genes.
Glucose homeostasis
GH affects glucose homeostasis with lipolysis and insulin resistance. Studies on
glucose homeostasis in GH-deficient adults revealed that insulin resistance may be
relatively common in these patients. However, the effect of GH replacement on
insulin resistance appears to depend on the duration and the dose of GH.
24