Page 24 - Banking Finance September 2025
P. 24
ARTICLE
young, typically between the ages of 20
and 35, and includes a growing number
of women, especially in freelance and
digital content creation roles.
Key Drivers of the GIG
Economy in India
Digital Transformation: India's digital
revolution-driven by cheap data, wide-
spread smartphone use, and expanding
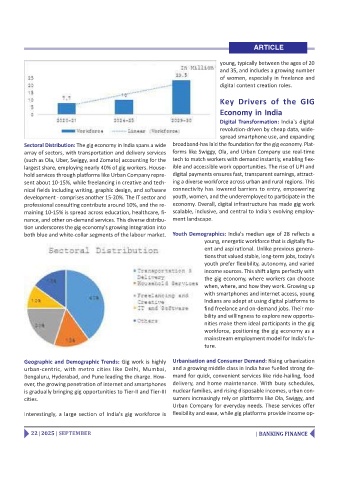
Sectoral Distribution: The gig economy in India spans a wide broadband-has laid the foundation for the gig economy. Plat-
array of sectors, with transportation and delivery services forms like Swiggy, Ola, and Urban Company use real-time
(such as Ola, Uber, Swiggy, and Zomato) accounting for the tech to match workers with demand instantly, enabling flex-
largest share, employing nearly 40% of gig workers. House- ible and accessible work opportunities. The rise of UPI and
hold services through platforms like Urban Company repre- digital payments ensures fast, transparent earnings, attract-
sent about 10-15%, while freelancing in creative and tech- ing a diverse workforce across urban and rural regions. This
nical fields including writing, graphic design, and software connectivity has lowered barriers to entry, empowering
development - comprises another 15-20%. The IT sector and youth, women, and the underemployed to participate in the
professional consulting contribute around 10%, and the re- economy. Overall, digital infrastructure has made gig work
maining 10-15% is spread across education, healthcare, fi- scalable, inclusive, and central to India's evolving employ-
nance, and other on-demand services. This diverse distribu- ment landscape.
tion underscores the gig economy's growing integration into
both blue and white-collar segments of the labour market. Youth Demographics: India's median age of 28 reflects a
young, energetic workforce that is digitally flu-
ent and aspirational. Unlike previous genera-
tions that valued stable, long-term jobs, today's
youth prefer flexibility, autonomy, and varied
income sources. This shift aligns perfectly with
the gig economy, where workers can choose
when, where, and how they work. Growing up
with smartphones and internet access, young
Indians are adept at using digital platforms to
find freelance and on-demand jobs. Their mo-
bility and willingness to explore new opportu-
nities make them ideal participants in the gig
workforce, positioning the gig economy as a
mainstream employment model for India's fu-
ture.
Geographic and Demographic Trends: Gig work is highly Urbanisation and Consumer Demand: Rising urbanization
urban-centric, with metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and a growing middle class in India have fuelled strong de-
Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune leading the charge. How- mand for quick, convenient services like ride-hailing, food
ever, the growing penetration of internet and smartphones delivery, and home maintenance. With busy schedules,
is gradually bringing gig opportunities to Tier-II and Tier-III nuclear families, and rising disposable incomes, urban con-
cities. sumers increasingly rely on platforms like Ola, Swiggy, and
Urban Company for everyday needs. These services offer
Interestingly, a large section of India's gig workforce is flexibility and ease, while gig platforms provide income op-
22 | 2025 | SEPTEMBER | BANKING FINANCE