Page 134 - Operations Strategy
P. 134
Six SigmA 109
● Beware of any approach that dismisses the contribution played by people in opera-
tions or processes. Even the originators of BPR later admitted that they had paid
insufficient attention to human resources within process. Because of this, the initial
impression (that BPR inevitably meant trampling over human aspirations and poten-
tial) became difficult to reverse.
Where does bPR fit into operations strategy?
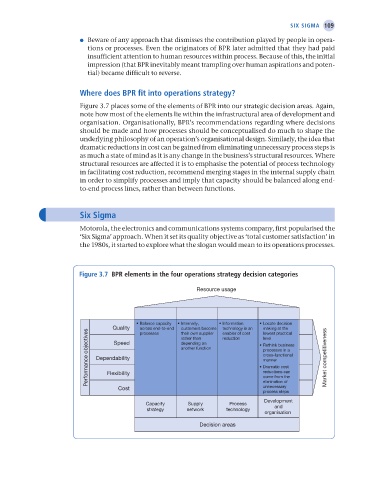
Figure 3.7 places some of the elements of BPR into our strategic decision areas. Again,
note how most of the elements lie within the infrastructural area of development and
organisation. Organisationally, BPR’s recommendations regarding where decisions
should be made and how processes should be conceptualised do much to shape the
underlying philosophy of an operation’s organisational design. Similarly, the idea that
dramatic reductions in cost can be gained from eliminating unnecessary process steps is
as much a state of mind as it is any change in the business’s structural resources. Where
structural resources are affected it is to emphasise the potential of process technology
in facilitating cost reduction, recommend merging stages in the internal supply chain
in order to simplify processes and imply that capacity should be balanced along end-
to-end process lines, rather than between functions.
Six Sigma
Motorola, the electronics and communications systems company, first popularised the
‘Six Sigma’ approach. When it set its quality objective as ‘total customer satisfaction’ in
the 1980s, it started to explore what the slogan would mean to its operations processes.
Figure 3.7 bPR elements in the four operations strategy decision categories
Resource usage
Balance capacity Internally, Information Locate decision
Quality across end-to-end customers become technology is an making at the
Performance objectives Dependability depending on Rethink business Market competitiveness
enabler of cost
their own supplier
processes
lowest practical
level
reduction
rather than
Speed
another function
processes in a
cross-functional
manner
Dramatic cost
Flexibility
reductions can
elimination of
unnecessary
Cost come from the
process steps
Development
Capacity Supply Process and
strategy network technology
organisation
Decision areas
M03 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 109 02/03/2017 13:03